Marketing tips, news and more
Explore expert-backed articles on SEO, data, AI, and performance marketing. From strategic trends to hands-on tips, our blog delivers everything you need to grow smarter.

Lazy Load: Improve Website Loading Performance
In order to increase the loading speed of the website, we will discuss the lazy-loading issue, which is recommended by Google and must be used. In order to increase site performance, the lazy load feature, which reduces the initial page load and load time, should be used, thanks to the method to be applied to the images and/or videos on the page.You will find answers to questions such as "What is lazy load?", "What are the advantages and disadvantages?", and "Why lazy load should be preferred and how can it be applied?" in this content.What Is Lazy Load?Lazy load is a technical method that allows the post-loading of non-critical images and videos while the web page is loading. Non-critical resources are loaded when they are needed or in their turn. Lazy loading is optional and has no negative effects on the web page when used correctly.If you have used the PageSpeed Insights tool, it gives you some suggestions to improve the performance of your web page on mobile and desktop devices. PageSpeed Insights offers you some opportunity suggestions to improve the performance of the page you are analyzing. Among these recommendations are warnings that sometimes "non-critical" or "off-screen images" should be postponed.At this point, PageSpeed Insights states that the lazy load technique should be used for the images on the website. If you have encountered the following events when visiting any website, you most likely have visited a lazy load page. Here are some symptoms of lazy load usage: Content comes as you scroll on the page you visit, As you scroll the screen, the image becomes clear and the real image is loaded, The image with optional lazy loading suddenly pops up in its turn. All websites, especially e-commerce websites, use the late loading technique of images.On the Medium website, the placeholder technique is used, in which a smaller image is added instead of the original image, and when the screen starts to scroll, the original image takes its place.SEO Tip: Lazy-loading should be applied to invisible images outside the screen, not the first images that appear when the screen is opened.Why is Lazy Load Used in Web Pages?Lazy load is used to prevent the site from loading late and to improve performance while the images or videos on the web pages are loading the page. The purposes of using lazy load are as such:When the lazy load is not used, it causes unnecessary data consumption while loading a web page and downloading images that the user may never see. Server requests will be reduced. For every resource on the web page, the server is requested to no avail while the page is loading. In this case, it affects the site performance negatively. If lazy-loading is not used on the web page, it wastes hardware resources for the browser to understand and decode the code content and place the image in the content. In order to improve the performance of the website, the lazy loading of images and videos, reducing the number of requests, resource consumption and data size reductions are among the factors that will positively affect the performance.Advantages of Using Lazy Load When you want to optimize your visual content on your website online, using lazy loading reduces memory usage and provides a good user experience. Unnecessary code execution on the web page is avoided. The reason is that the content will be loaded in its turn. For website owners, it can reduce the resource cost as the request to the server is reduced. Disadvantages of Using Lazy Load The lines of code to be added to lazy-load images after the website is set up can confuse you when interpreting the code. Misuse can prevent your content from appearing in search engines. How to Apply Lazy Load to Pictures and Videos?There are different methods for applying the lazy-loading feature to the images on the web page. Modern web browsers lazy-load images and videos on web pages at the browser level. In older browsers, there are auxiliary javascript libraries to use the lazy load technique.What is Browser-Level Lazy Loading?Browser-level lazy loading for web pages is when modern browsers have coded lazy loading built into the background. Modern browsers are actively used in browsers such as Chrome, Firefox, Edge, and Opera with chromium support.For example, in modern browsers, to make images below the viewport load at a lower priority, simply add the loading attribute to the img and iframe elements.With the loading feature above, you do not need to add an extra library in the source code of your website for modern browsers.Using Lazy Load for PicturesIn HTML, two methods are used to include images on a web page. Images are loaded on web pages with CSS as a background image or element. Let's examine how the lazy load feature is implemented for both image loading methods.Using Lazy Load for Image ElementWhile adding the lazy load feature to the inline element in HTML, you can take advantage of the JavaScript libraries for modern browser-level lazy load or lazy load. We have included our example for browser-level installation in the previous topic. For older browsers, you can use JavaScript libraries.Using Lazy Load for Background ImageIn some websites, some images are used as background images with the help of CSS. Although this situation is not recommended in terms of SEO, it is a situation that should be considered in indirect SEO studies.The best solution for this situation is to load an image much smaller in size instead of the background image until it's time. It will be replaced by the original picture when it is their turn.Using Lazy Load for VideosAs in visual media, it can be ensured that videos are loaded late on web pages containing videos. The best usage method for this method is to activate the videos by the users.Google's Perspective on Lazy LoadGoogle says that the use of lazy-loading is among the best practices in terms of increasing performance and user experience when it comes to late loading of off-screen images on the web page. However, Google also says that this technique will cause the content to be hidden in Google if used incorrectly. In order for Googlebot to see all the content on the web page, make sure that the content is displayed while it is being viewed.Lazy Load Plugin Recommendation for WordPress WebsitesFor WordPress website owners, we recommend using the native lazy load plugin released by Google. After adding the plugin to your website, you do not need to take any additional action. The loading="lazy" attribute will be automatically added to all images and iframes on your website.Thanks to this simple and useful plugin, Googlebot will have no problem indexing lazy-loaded images on your website without any problems.How to Install Lazy Load?Lazy load installation varies according to the infrastructure of your website. If you have a WordPress website, you can follow the steps below on how to set up Lazy Load to snooze off-screen pictures. Login to the WordPress admin panel Click on Plugins > Add New button Type "Native Lazyload" in the "Search for plugins..." field Click the "Install Now" button to install the add-on Click the "Activate" button after the installation is complete That's how easy the installation is! This plugin that you install to optimize the WordPress website will take care of everything automatically for you.If there is no CMS website, add the JS file URL of the lazyload library you want to use between the tags of your site to install lazyload. Then just write "lazyload" to your image's class.ConclusionWhen the lazy load feature is used carefully and correctly, lazy-loaded images and videos can reduce the file size downloaded during the initial web page load time and on-page load.Users who visit the website can sometimes leave the site without scrolling to sub-pages in the content. Lazy loading leads to both network demand and resource usage, as images below the screen are downloaded on unused sites.If the web page contains too many images, lazy loading is a very good technique to improve the performance of your website on the PageSpeed Insights side.

Sustainability in E-Commerce
Sustainability is not a factor that can be ignored in e-commerce—it must not be. The rising trend of environmental sustainability is humanity’s reflex against the destructive “grow or die” imperative of capitalism. In e-commerce, sustainability can span from business models to packaging materials, and with younger generations increasingly taking the lead, it will become ever more important in the years ahead.Awareness of environmental issues and sustainability has long been a trend in global e-commerce. To successfully meet growing consumer demands for sustainability, online retailers have been focusing on topics such as corporate social responsibility and eco-friendly approaches within their supply chains.In this article, we will cover: What Is Sustainability? Sustainability in the E-Commerce Sector How the New Generation Views Sustainability Example Brands What Is Sustainability? (Revisited) “Sustainability,” a concept we’ve been hearing about increasingly in recent years, aims—as its name suggests—to ensure that all living beings around the world can continue to exist indefinitely. The ultimate goal is to build a world where we do not compromise today’s standard of living, where future generations can equally benefit, where resources are used in a controlled manner, and where everyone can live healthily and happily. Every effort—including those in e-commerce—must be in harmony with nature. No individual or corporate action should disrupt ecological balance; rather, it should directly or indirectly contribute to its long-term stability. A. Getting Started in E-CommerceE-commerce has spread rapidly worldwide since the 1990s. In Turkey, it has become especially popular over the last 20 years. Naturally, with this boom in online shopping comes an increase in waste materials. Shipping boxes, plastic bags, branded plastic wraps from courier companies, and so on accumulate as large piles of recyclable or non-recyclable waste. In this situation, traditional businesses moving into e-commerce have begun to focus more on eco-friendly practices and must become increasingly cautious about sustainability.B. Sustainability Around the WorldScientists and international bodies have made broad calls and warnings urging humanity to protect nature and ensure sustainable living on Earth. These calls demand fundamental changes and urgent measures to avoid further environmental harm. Ensuring and supporting sustainable living has become inevitable for nations. Therefore, while maintaining economic development, countries must avoid actions that harm the environment and develop strategic plans for sustainable development. The urgency of sustainable development grows daily. Many international organizations are actively working on sustainability. Bodies such as the European Union (EU) and the United Nations (UN) have mobilized to promote sustainable growth, devising various strategies and policies. Under its Europe 2020 strategy, the European Commission defined three main growth priorities, one of which is “promoting a more resource-efficient, greener, and more competitive economy.” Meanwhile, the United Nations took an even more comprehensive step. In 2000, the UN set the Millennium Development Goals (MDGs) and in 2015 expanded them into the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs). The SDGs are considered the most comprehensive action plan for nations to achieve sustainable development. These goals are financially supported by the World Bank Group (2017) and the International Monetary Fund (IMF, 2020). In September 2015, the UN adopted 17 SDGs as core components of the 2030 Agenda for Sustainable Development—extended versions of the MDGs that concluded at the end of 2015. All UN member states committed to building a sustainable future encompassing the three dimensions of development: environmental, social, and economic.C. Reducing Carbon FootprintLogistics—especially transportation by truck or plane—relies heavily on fossil fuels, increasing carbon emissions. Reducing carbon footprints helps slow and mitigate global warming. In Turkey, a prime example of a company leading carbon footprint reduction is Yemek Sepeti. Handling millions of orders daily, they removed single-use plastic cutlery, drastically cutting plastic waste. Another notable example is Koton, which redesigned its cardboard packaging for multiple uses, thereby reducing its carbon footprint. LC Waikiki launched a project to transform its shipping boxes into toys for children, further promoting sustainability.On their website, LC Waikiki describes the initiative:“LC Waikiki is preparing to win children’s hearts with its new project. According to a LinkedIn post by E-commerce General Manager Ömer Barbaros Yiş, the brand’s shipping boxes will now become toys.”This initiative, while still under development, hints at a creative approach to reducing waste and enhancing customer engagement.D. The New GenerationThe 1970s hippie movement introduced environmental respect and sustainability topics to the wider public. In the 1990s, as e-commerce spread globally, discussions of sustainability in online retail began in earnest. Millennials—born in the ’80s and ’90s—are generally more aware and conscientious than earlier generations (Baby Boomers and Generation X). Economic crises and environmental disasters (e.g., Amazon deforestation, melting glaciers, wildfires in Australia and elsewhere) have made Generation Z even more attentive to sustainability. Generation Z, born into the internet era, often shops online as a matter of course—and sometimes even more than offline. For them, sustainability in e-commerce is critically important. Knowing this, both legacy retailers and pure-play e-commerce startups are embracing sustainability practices as both a business strategy and a demonstration of respect for the environment.E. Sustainable E-Commerce in TurkeyE-commerce has existed in Turkey for over 20 years, but initial distrust of the internet slowed its growth. Over the past five years, sales have surged, especially during the COVID-19 pandemic, mirroring global trends. Because e-commerce developed later in Turkey than in many other countries, both traditional retailers moving online and new e-commerce ventures are rapidly adapting and innovating to meet consumer expectations.Example BrandsSome Turkish companies leading the way in sustainable e-commerce include:E-BebekE-Bebek is often the first name that comes to mind regarding sustainability in Turkey. According to an Instagram post by Sertaç Doğanay, they introduced “detergent refill centers” in major stores. Customers bring their own containers to refill detergent at prices lower than retail, reducing single-use plastic waste and embracing an eco-friendly commerce model. MaviMavi took a step by switching from disposable plastic shipping bags to resealable, reusable pouches, minimizing plastic usage. They also launched the “Mavi Transformation” project, turning 593,750 recycled PET bottles into high-quality denim through their expertise. CEO Cüneyt Yavuz stated: “Using innovation and technology, we’re transforming denim and aim for 100% sustainable All Blue products by 2030.”LC WaikikiLC Waikiki’s “Green Collection” of eco-friendly, organic apparel demonstrates its commitment to sustainability. They also announced plans to convert shipping boxes into toys, as hinted by E-commerce GM Ömer Barbaros Yiş on LinkedIn.Boyner GroupBoyner Group highlights its sustainability and CSR efforts under four pillars: Social Impact, Environmental Impact, Workplace Democracy, and Our Value Chain. They publish transparent sustainability reports from 2008 to 2020, showcasing their eco-friendly initiatives and commitment to a sustainable future.If you found this blog post on sustainable e-commerce helpful, please share it on social media so others can benefit!
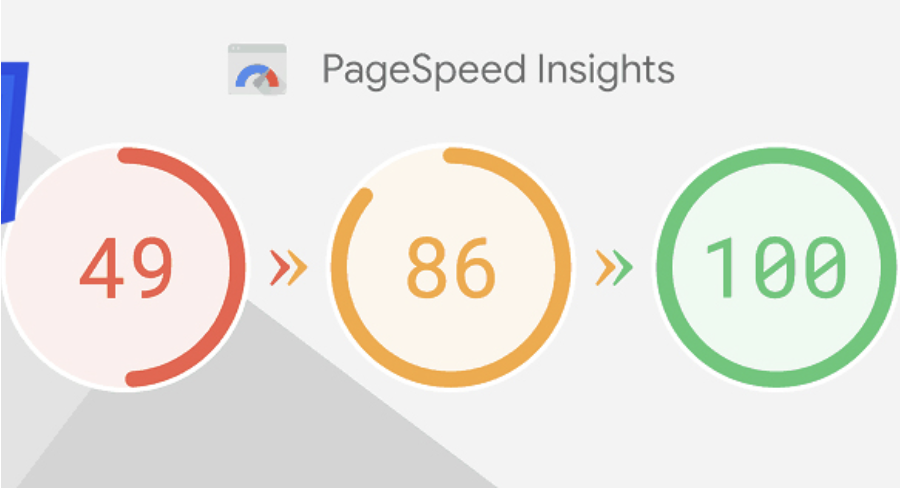
How to Fix Remove Unused CSS Warning
Updates in search engine algorithms have made many metrics and technical infrastructure important to provide a more successful user experience. In the period from 2015 to 2022, users' mobile and tablet usage increased significantly, while desktop and laptop usage decreased. This situation has caused poor user experiences, especially on sites with large page sources.For example, users visiting a website from mobile devices experience excessive resource consumption and wasted time while loading websites with high-volume images and unused CSS and JS files. This is because the loading times and site speeds of such websites provide an inadequate experience for users, and since the user accesses the site from a search engine, it also causes search engines to lose image.Aware of this, search engines have started to pay significant attention to website speed and resource consumption with the latest updates in their algorithms. To optimize this situation, website owners have strengthened their optimizations in this regard by analyzing the speed and resource consumption of their websites with measurement tools such as Pagespeed and GTMetrix.Pagespeed Page Speed AnalysisAmong the most important performance tools used when optimizing a website, Pagespeed and GTMetrix tools undoubtedly come first. Pagespeed, in particular, developed by Google, shares with us the speed metrics that prevent a successful user experience on websites.One of the metrics that website owners frequently encounter and often fail to solve in Pagespeed analyses is the removal of unused CSS files.Unfortunately, Pagespeed and GTMetrix tools do not share with us which lines in the unused CSS files are actively used, but only provide us with estimated savings and files. This warning alone is not enough to solve this problem.What Are Unused CSS Files?In today's modern web programming technologies, many developers prefer ready-made libraries instead of coding HTML & CSS from scratch. Libraries like Boostrap and Tailwind are examples of these structures. The difference of ready-made CSS libraries is that they collect many button, navbar, grid structure, visual and design commands under certain classes in a single library. In this way, web site developers can easily use all style and CSS arrangements by giving a class to the relevant HTML element, instead of writing separate CSS commands for each structure and module. For example, while many lines of CSS code need to be written to give a button various color and radius styles and hover effects, the desired style arrangements can be obtained by giving a single class since the relevant commands and lines are included in the ready-made library.Although ready-made CSS libraries are very practical for developers, they can cause some problems in SEO-related arrangements as they increase the query and resource consumption on the website. For example, when you include the bootstrap library on your website, you can actively use only 1 or 2 of the 16 different button styles in it. The remaining 14 button styles continue to be included in the CSS file and increase the page's resource consumption even though they are not actively used.In these cases, performance tools that measure speed, such as PageSpeed, inform us that there are actively unused CSS files on the website and ask us to make optimizations related to this.How to Detect Unused CSS Files?There are several ways to detect unused CSS lines on a website. You can use modules like purgeCSS or manually view these lines from the page inspection.To detect unused CSS files, the first thing you need to do is right-click on the page and click on the "Inspect" option.Then click on the three dots on the right side of the window that opens and click on the More Tools > Coverage option.You will see a record button in the section that opens at the bottom. Click this button and refresh the page with CTRL + F5 or Command + F5. After the page is refreshed, you will see that many CSS and JS files have appeared below.The rates on the right side in this section show the unused rate in the relevant CSS file at the moment the page is loaded.When you click on any CSS file, the relevant file opens in the window, and you can again view the unused CSS lines in red and the actively used ones in blue.The important detail here is to determine which code is used on different pages and which lines are active on mobile and tablet devices.How to Remove Unused CSS Files?We learned where to see the unused CSS lines on the website. However, the important part here is to be able to analyze well which CSS line is really used and which is not. Because some CSS lines may be included in a single file for different pages, as well as being included in mobile and tablet devices.For this reason, you should first copy the unused lines from the ready-made library codes in the CSS lines, then navigate to the service, category, product, contact, etc. pages of the site and perform the coverage process we shared above on each page.In addition to this process, you should switch to the mobile and tablet views of your website from the device selection area in the inspect section and, in the same way, visit all pages and copy the unused CSS lines to one side.In the final stage, you can clean the common and actively unused CSS lines among all the CSS lines you have copied.Note: It is recommended that you perform all these operations on the test version of your website and, after performing the cleaning, carry it to the main version if no problems are observed.

What is Google Search Console? How to Use Google Search Console?
Google Search Console can be defined as a free Google Webmaster tool, available to anyone who owns a website. Of course, that definition is very general. More precisely, Google Search Console is a tool that allows site owners to check and optimize their website’s presence on Google.In this article, we will answer many common questions about Google Search Console.What is Google Search Console?Let’s take a closer look at what Google Search Console really is, beyond the general outline above.Google Search Console is a free Google service useful to anyone with any relationship to Google on the web. Formerly called Google Webmaster Tools, it evolved into today’s Search Console as each tool was specialized. Another useful free tool provided by Google is Google Analytics. Search Console and Google Analytics used to be integrated directly.With Google Search Console, you can see how Google views your site. You can also access detailed performance data—such as which queries drive how much organic traffic—which pages rank for which keywords.Search Console isn’t just for site owners; content creators benefit too. Ranking issues can arise from technical errors, preventing valuable content from appearing correctly in search results. Search Console helps diagnose and fix such issues for individual pages or entire sites.To use Google Search Console, you need a Google account. Simply go to https://search.google.com/search-console/ and sign in with your Google credentials.On your first visit, you’ll see a screen like the one above, where you can add the sites you own to your Search Console account.Adding a Site to Search ConsoleAfter setting up your account, you must add your site to Search Console to verify ownership. The steps are as follows:You have two options here. “Domain” verifies all subdomains and protocols under that domain in one property. “URL prefix” verifies only the exact URL you specify. Because some sites require separate entries for https:// and http:// under “Domain,” you may prefer “URL prefix” to avoid duplicate properties.Site Verification MethodsSearch Console offers several methods to verify you own the site. All methods confirm that the person requesting Search Console access has control over the site’s code or files. In every case, you must either upload a file or add code that only the site administrator can do.HTML File UploadAfter entering your site URL and choosing verification, you can download a unique HTML file from Google. Upload that file into your site’s root directory (usually public_html), then click “Verify.”Once Google can fetch that file, you’ll see a “Ownership verified” message. If you later remove the file, verification will expire and you’ll lose Search Console access.HTML Meta TagYou can also verify by adding a meta tag to the section of your site’s homepage.Paste Google’s unique verification code into your , click “Verify,” and you’ll gain access immediately.Other methods include: Google Analytics: Verify if you already have Analytics tracking set up. Google Tag Manager: Use your GTM container snippet to verify. Domain name provider: Add a DNS TXT record at your domain registrar. Adding the Correct PropertyA common pitfall is adding duplicate properties—for example, both https://analyticahouse.com and https://www.analyticahouse.com. Technically they are different URLs. The canonical version should be used, or add the domain property to cover all variants in one go.Search Console TerminologyWhat is a Search Query?Every keyword search that returns your site in results is counted as a query. Search Console shows which queries your site appears for, along with performance metrics.ImpressionsAn impression is counted each time a URL from your site appears in a user’s search results. The user doesn’t even need to scroll down; merely being listed counts as one impression.ClicksA click is when a user clicks through from the search results to your page. Repeat clicks in the same session don’t count; clicks from different sessions or after clicking another result will count again.Average PositionThis is the average ranking position of your pages for a given query or set of queries. For example, if one page ranks 7th for “Google Algorithm” and 5th for “Algorithm Updates,” its average position would be 6.CTR (Click-Through Rate)CTR is clicks divided by impressions, expressed as a percentage. If you get 50 clicks from 100 impressions, your CTR is 50%.Key Filters in Search ConsoleSearch TypeFilter performance by search type: Web, Image, Video, or News. You can also compare two search types side by side.Date RangeFilter data by date range—last 7 days, last 28 days, last 3 months, etc.—or compare two ranges for trend analysis.Query, Page, Country, DeviceUnder “New” you can filter by specific queries, pages, countries, or devices (desktop, mobile, tablet).Index Coverage ReportThis report shows which pages Google successfully indexed, which have errors, and which were excluded (e.g., due to canonical tags).Submitted SitemapsSee which sitemaps you submitted and whether Google could read them successfully.Common Uses of Search Console DataHere are the most frequent ways to leverage Search Console for SEO: Identify pages with the most organic clicks Find queries with the highest CTR Track CTR trends over time Monitor impressions over time Discover pages with the highest rankings Spot pages with declining rankings Detect ranking improvements or drops Find queries driving the most traffic Compare performance across desktop, mobile, and tablet Check how many pages are indexed vs. have indexing issues Detect mobile usability issues See total backlinks Identify which URLs have the most backlinks Inspect how Googlebot fetches a specific URL Top Organic Pages by ClicksGo to Performance → Pages, set your date range (e.g., last 12 months), check only the Clicks metric, and sort descending.Queries with Highest CTRIn Performance → Queries, set your date range, check only CTR, and sort descending.Track CTR Over TimeIn Performance, view the CTR line chart to catch sudden drops or spikes, which may indicate changes in rankings or impression volume.Track Impressions Over TimeSimilarly, the Impression chart reveals whether you’re gaining visibility for more keywords or losing ground.Pages with Highest Average PositionIn Performance → Pages, set date range to last 28 days, check only Average Position, and sort ascending.Pages with Lowest Average PositionSame steps as above, but sort Average Position descending to find underperforming pages.Detect Ranking ChangesUse the date comparison in Performance → Queries to spot keywords that rose or fell between two periods.Top Traffic-Driving QueriesIn Performance → Queries, set date range, check Clicks, and sort descending.Device ComparisonIn Performance → Devices, check all metrics to compare desktop, mobile, and tablet performance side by side.Indexed vs. ErrorsIn Coverage, see how many pages are valid (indexed) versus errors (not indexed).Mobile Usability IssuesIn Mobile Usability, view any pages with mobile errors.Total BacklinksUnder Links → External, click “More” and view the total number of backlinks.Top Linked PagesIn the same report, sort “Top linked pages” by descending links.URL InspectionUse the URL inspection box at the top to see how Googlebot fetches a specific URL and whether it’s indexed.ConclusionGoogle Search Console is an essential SEO tool, playing an active role in diagnosing and improving a site’s interaction with Google search. We’ve covered its most common uses, but Search Console offers much more. As Google continues to enhance this tool, familiarity with Search Console is becoming mandatory for anyone working in digital marketing or web development.

Log File Analysis for SEO Performance
From an SEO performance perspective, log file analysis—and specifically examining the server’s access logs—tells us exactly how search engine bots behave after they crawl our site.In this article, we’ll answer “How do you perform a detailed log file analysis for SEO?” and “What are the benefits of log analysis?” using various scenario-based examples.What Is a Log File?Log files record who accessed your site, when, from which IP, and which URLs they requested.“Visitors” includes not only human users but also Googlebot and other search engine crawlers.Your web server writes these logs continuously and rotates or overwrites them after a set period.What Data Does a Log File Contain?A typical access log entry looks like this:27.300.14.1 – – [14/Sep/2017:17:10:07 -0400] “GET https://allthedogs.com/dog1/ HTTP/1.1” 200 “https://allthedogs.com” “Mozilla/5.0 (compatible; Googlebot/2.1; +http://www.google.com/bot.html)”Depending on your server configuration, you might also log response size or request latency. A breakdown of the key fields: IP address of the requester Timestamp of the request Method (GET or POST) Requested URL HTTP status code (see HTTP status codes) User-Agent string, telling you the client or crawler type Googlebot IP Address ListIn November 2021, Google published the full list of IP ranges it uses to crawl websites. You can find the JSON here:https://developers.google.com/search/apis/ipranges/googlebot.jsonWhere to Find Your Log FilesLogs live on your web server or—in some cases—on your CDN. How you access them depends on your server stack (nginx, Apache, IIS) and control panel. For example:cPanel: /usr/local/apache/logs/ or via the “Raw Access Logs” featurePlesk: /var/www/vhosts/system/your-domain.com/logs/Why Is Log Analysis Important for SEO?Analyzing logs tells you exactly which URLs search bots actually fetch—and whether they encounter errors.Unlike tools like Screaming Frog or DeepCrawl, which follow links, bots revisit URLs they’ve previously seen. If a page existed two days ago but now 404s, only logs reveal that mismatch.Log analysis can show you: Which pages bots crawl most often (and which they ignore) Whether bots encounter 4xx or 5xx errors Which orphaned (unlinked) pages are still being crawled Tools for Log File AnalysisPopular log analysis tools include: Splunk Logz.io Screaming Frog Log File Analyser (free up to 1,000 lines) Semrush Log File Analyzer GSC Crawl Stats vs. LogsGoogle Search Console’s Crawl Stats report shows some high-level crawl data, but it’s nowhere near as granular as raw logs.To access it: Settings > Crawling > Open report.Interpreting Crawl Stats Status All good: No crawl errors in the last 90 days Warning: An error occurred more than 7 days ago Critical: Errors detected within the last 7 days The report also breaks down by status code, file type, and crawler type (desktop, smartphone, AdsBot, ImageBot, etc.).How to Interpret Your Log AnalysisWith logs, you can answer: What percentage of my site do bots actually crawl? Which sections never get crawled? How deep into my site do bots venture? How often do they revisit updated pages? How quickly are new pages discovered? Did a site structure change affect crawl patterns? Are resources (CSS, JS) delivered quickly? 7 Example ScenariosHere are seven practical ways log analysis can inform your SEO strategy:1. Understand Crawl BehaviorCheck which status codes bots see most often and which file types they request. For example, in Screaming Frog’s log report: 2xx codes on HTML/CSS/JS are ideal—pages load successfully. 4xx codes indicate broken links or removed pages—these can waste crawl budget. 3xx codes show redirects—make sure only necessary redirects remain. 2. Identify Your Most Important PagesBots allocate more crawl budget to pages with more internal or external links. If you see excessive crawl on an English subdirectory, for instance, you might adjust your navigation or internal linking.3. Optimize Crawl BudgetEven smaller sites benefit from eliminating waste. Use logs to find URLs with unnecessary parameter crawls, frequent 301s, or robots.txt misconfigurations. Remove parameterized URLs from your sitemap and internal links. Set long Cache-Control headers for static assets. Consolidate multiple redirects into a single chain. Fix robots.txt typos so bots respect your crawl rules. 4. Detect Crawl ErrorsHigh volumes of 4xx/5xx responses can cause bots to throttle or stop crawling. Compare 2xx vs. error rates and fix broken pages promptly.5. Find Crawlable but Unindexed PagesPages eligible for indexing but rarely crawled can be found by filtering logs on low crawl frequency—e.g. “XX weeks ago.”Add these pages to your sitemap, link to them internally, and refresh their content.6. Discover Orphan PagesOrphan pages (unlinked) may still appear in logs. Filter logs for 200-OK HTML URLs with zero internal referrers. Then add internal links or remove them if they aren’t needed.7. Aid Site MigrationsDuring a migration, logs show your most-crawled URLs so you can prioritize preserving their redirect paths. After migration, logs reveal which URLs bots can no longer find.Using Log Analysis to Drive SEO FixesBy acting on your log insights, you can: Remove non-200 URLs from your sitemap Noindex or disallow low-value pages Ensure canonical tags highlight key pages Boost crawl frequency by adding internal links to strategic pages Guarantee all internal links point to indexable URLs Free up crawl budget for new and updated content Verify category pages are crawled regularly ConclusionLog file analysis is a powerful way to discover hidden SEO issues and refine your crawling strategy. If you found this guide helpful, please share it on social media so others can benefit!
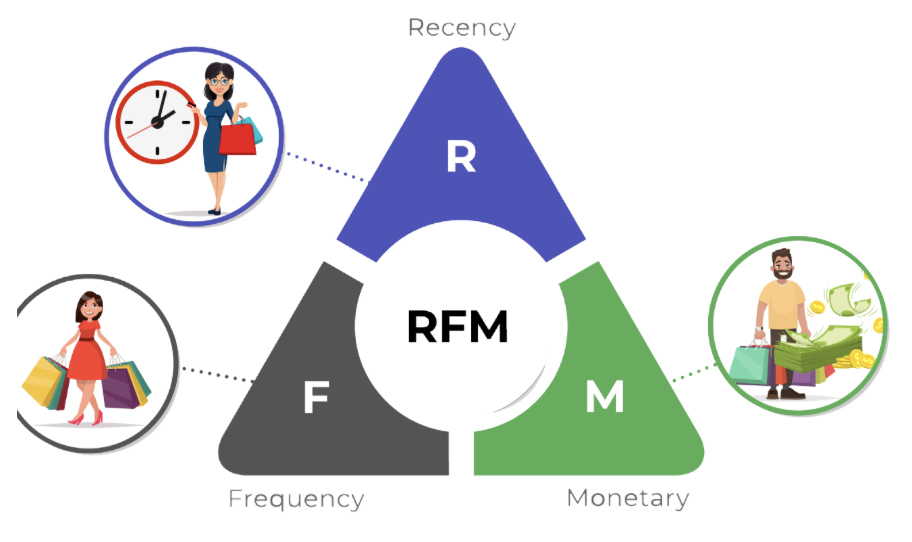
What is RFM Analysis?
What is the most valuable asset for a company? Its tangible assets or inventory? Given developments in supply chains and the level of financial solutions, if you’re especially an e-commerce business, your most valuable asset is your customers.Beyond your sales, when planning your inventory levels, ad investments, and many operational activities, you must consider the future behavior of your customers.In today’s age of increasing digitalization and personalization, getting to know your customers is easier thanks to big data—but it also becomes more challenging as customer volume and diversity grow.In this article, we’ll discuss RFM analysis, one of the fundamental analyses you can use to segment your customers and build effective audiences.What Is RFM Analysis?RFM analysis segments customers based on purchase data. As an algorithm, it uses unsupervised clustering (K-means). The “RFM” acronym stands for three key metrics. First, let’s look at what each metric means.RecencyCalculated by the number of days between the analysis reference date and the customer’s most recent purchase date.FrequencyThe number of purchases the customer made in the analysis period. If many customers purchased only once—skewing the distribution—you may treat one-time buyers separately for a healthier analysis.MonetaryThe total monetary value of the customer’s purchases in the analysis period. Two considerations: 1) If purchases are in multiple currencies, convert them to a single currency. 2) If you have B2B wholesale orders, exclude them so they don’t skew the distribution.What Questions Can RFM Analysis Answer?Although RFM is purchase-behavior–based, it can answer many strategic questions about both new and existing customers, for example: Who are our most valuable customers? Which customers are at risk of churn? Which customers deserve retention efforts? Which customers share similar behavior for targeted campaigns? Why Is RFM Analysis Important?As every marketer knows, retaining existing customers is far cheaper than acquiring new ones. By using RFM to gauge how close customers are to conversion or churn, you can both retain at-risk customers and encourage more spending among active customers. You can also classify newly acquired customers into existing RFM segments to start personalized marketing before you’ve collected much new data.Required Data StructureRFM relies on transaction data—either CRM order logs or analytics platform transaction exports. For robust results, use at least one year (ideally two) of data. You need these columns: Unique customer identifier (user_id) Transaction date Order ID Transaction amount Then compute per-customer Recency, Frequency, and Monetary values in your database or analytics tool.Segmenting and Labeling AudiencesCluster customers into, say, four groups by each R, F, and M metric. Then combine their cluster labels. For example:Customers with high Frequency and high Recency are “Champions,” while high Frequency but low Recency might be “At Risk” or “Can’t Lose Them.” You can send “We miss you” coupons to at-risk groups, and premium product offers to Champions.Sum the R, F, and M cluster scores to get an overall customer score, then bucket into “Platinum,” “Gold,” “Silver,” etc. Use these segments to allocate ad budgets more effectively.At its core, RFM groups similar shoppers so you can optimize marketing spend, guide retention, and forecast sales.Additional Metrics to ConsiderYou can extend RFM with: Duration/Engagement: session time or pages per session Tenure: days since first purchase Churn Risk: predicted probability of churn Adding these refines your segments and deepens insights.Next StepsOnce segments are defined, analyze demographic, geographic, and behavioral patterns within each. Then: Map new customers to existing segments for immediate targeting. Run category- or product-level RFM to create niche micro-segments. Apply attribution models to understand each segment's purchase journey and optimize touchpoints. RFM analysis offers actionable insights from simple transaction data—use it to refine marketing strategies, reclaim at-risk customers, and boost customer lifetime value.If you found this post useful, please share it on social media so others can benefit!References https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/RFM_(market_research) https://www.investopedia.com/terms/r/rfm-recency-frequency-monetary-value.asp https://iopscience.iop.org/article/10.1088/1742-6596/1869/1/012085/pdf

