
Analytica House
Sep 4, 2022What is Google Search Console? How to Use Google Search Console?

Google Search Console can be defined as a free Google Webmaster tool, available to anyone who owns a website. Of course, that definition is very general. More precisely, Google Search Console is a tool that allows site owners to check and optimize their website’s presence on Google.
In this article, we will answer many common questions about Google Search Console.
What is Google Search Console?
Let’s take a closer look at what Google Search Console really is, beyond the general outline above.
Google Search Console is a free Google service useful to anyone with any relationship to Google on the web. Formerly called Google Webmaster Tools, it evolved into today’s Search Console as each tool was specialized. Another useful free tool provided by Google is Google Analytics. Search Console and Google Analytics used to be integrated directly.
With Google Search Console, you can see how Google views your site. You can also access detailed performance data—such as which queries drive how much organic traffic—which pages rank for which keywords.
Search Console isn’t just for site owners; content creators benefit too. Ranking issues can arise from technical errors, preventing valuable content from appearing correctly in search results. Search Console helps diagnose and fix such issues for individual pages or entire sites.
To use Google Search Console, you need a Google account. Simply go to https://search.google.com/search-console/ and sign in with your Google credentials.
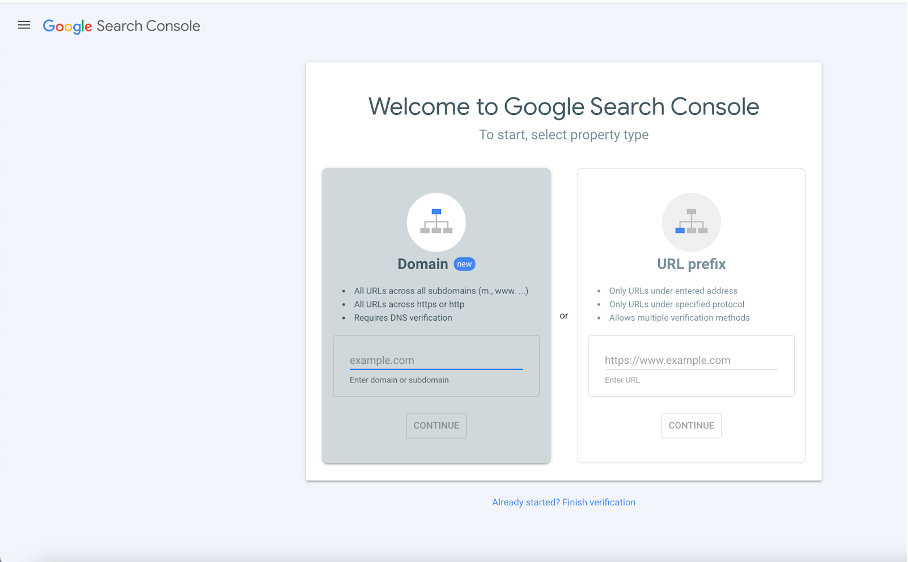
On your first visit, you’ll see a screen like the one above, where you can add the sites you own to your Search Console account.
Adding a Site to Search Console
After setting up your account, you must add your site to Search Console to verify ownership. The steps are as follows:
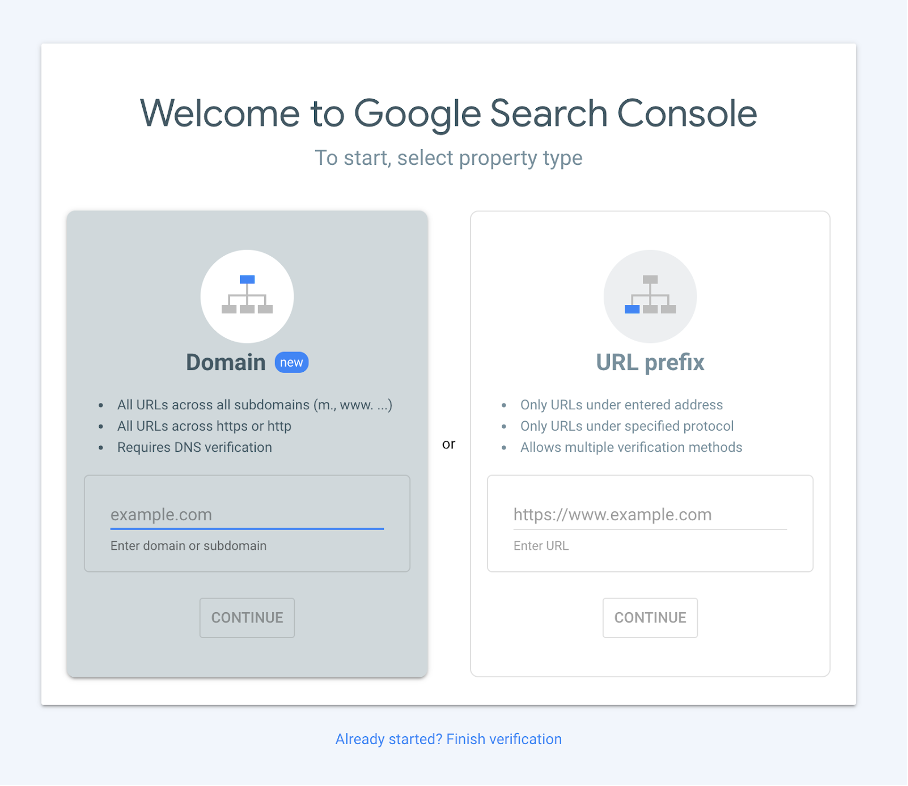
You have two options here. “Domain” verifies all subdomains and protocols under that domain in one property. “URL prefix” verifies only the exact URL you specify. Because some sites require separate entries for https:// and http:// under “Domain,” you may prefer “URL prefix” to avoid duplicate properties.
Site Verification Methods
Search Console offers several methods to verify you own the site. All methods confirm that the person requesting Search Console access has control over the site’s code or files. In every case, you must either upload a file or add code that only the site administrator can do.
HTML File Upload
After entering your site URL and choosing verification, you can download a unique HTML file from Google. Upload that file into your site’s root directory (usually public_html), then click “Verify.”
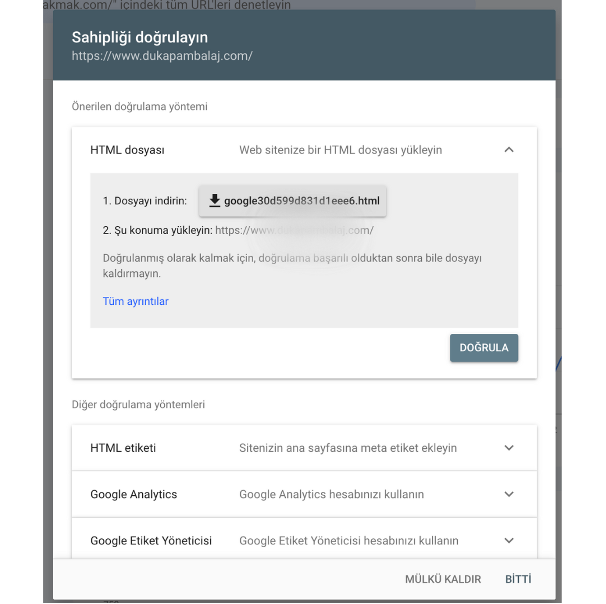
Once Google can fetch that file, you’ll see a “Ownership verified” message. If you later remove the file, verification will expire and you’ll lose Search Console access.
HTML Meta Tag
You can also verify by adding a meta tag to the section of your site’s homepage.
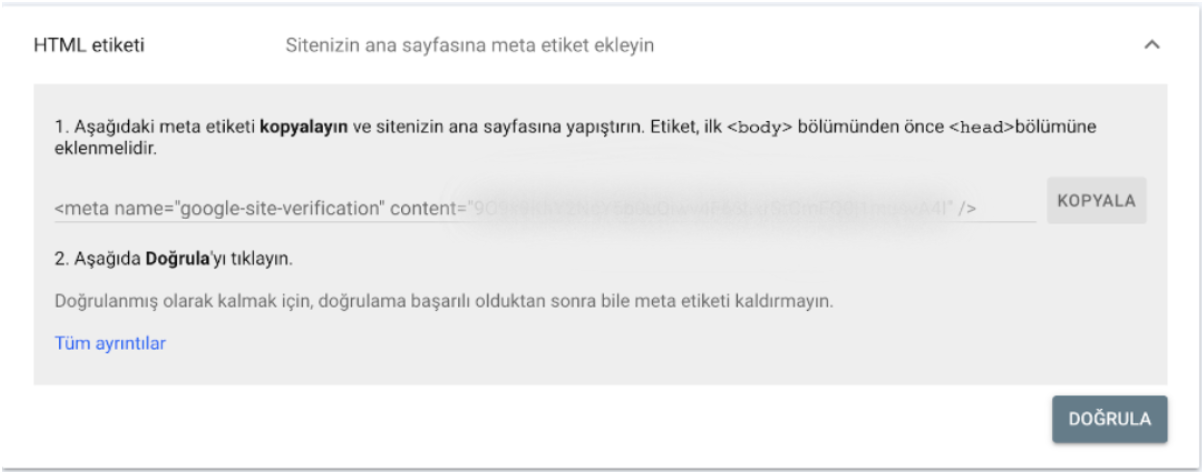
Paste Google’s unique verification code into your , click “Verify,” and you’ll gain access immediately.
Other methods include:
- Google Analytics: Verify if you already have Analytics tracking set up.
- Google Tag Manager: Use your GTM container snippet to verify.
- Domain name provider: Add a DNS TXT record at your domain registrar.
Adding the Correct Property
A common pitfall is adding duplicate properties—for example, both https://analyticahouse.com and https://www.analyticahouse.com. Technically they are different URLs. The canonical version should be used, or add the domain property to cover all variants in one go.

Search Console Terminology
What is a Search Query?
Every keyword search that returns your site in results is counted as a query. Search Console shows which queries your site appears for, along with performance metrics.
Impressions
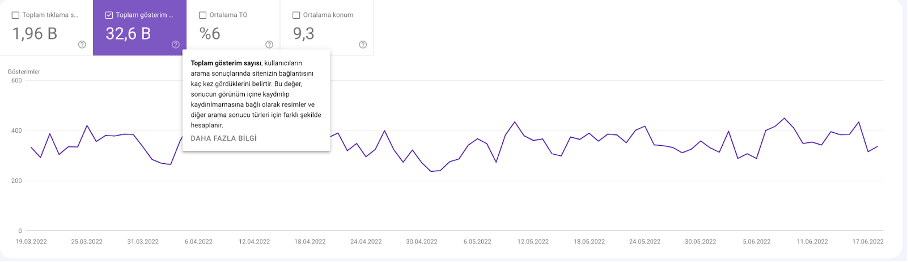
An impression is counted each time a URL from your site appears in a user’s search results. The user doesn’t even need to scroll down; merely being listed counts as one impression.
Clicks
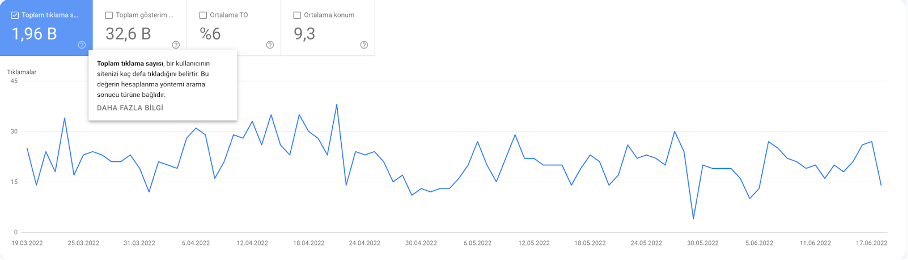
A click is when a user clicks through from the search results to your page. Repeat clicks in the same session don’t count; clicks from different sessions or after clicking another result will count again.
Average Position
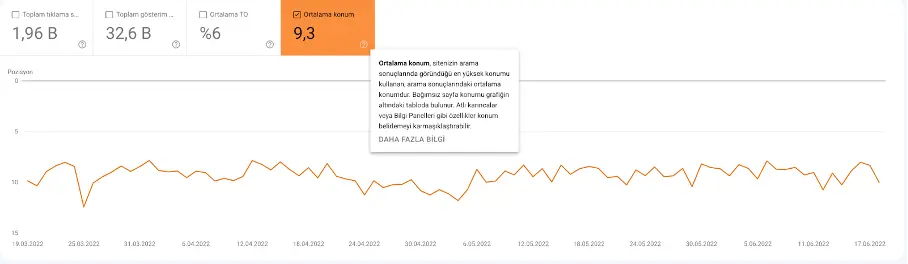
This is the average ranking position of your pages for a given query or set of queries. For example, if one page ranks 7th for “Google Algorithm” and 5th for “Algorithm Updates,” its average position would be 6.
CTR (Click-Through Rate)
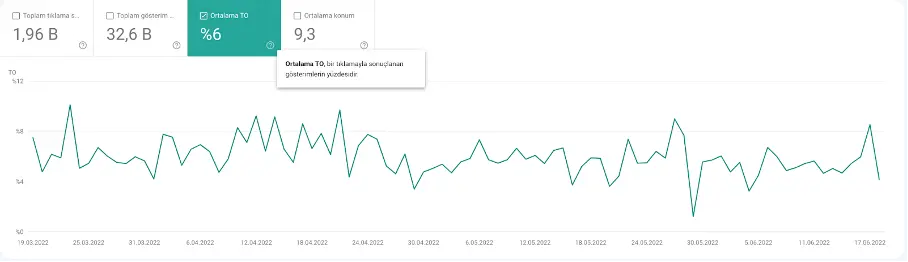
CTR is clicks divided by impressions, expressed as a percentage. If you get 50 clicks from 100 impressions, your CTR is 50%.
Key Filters in Search Console
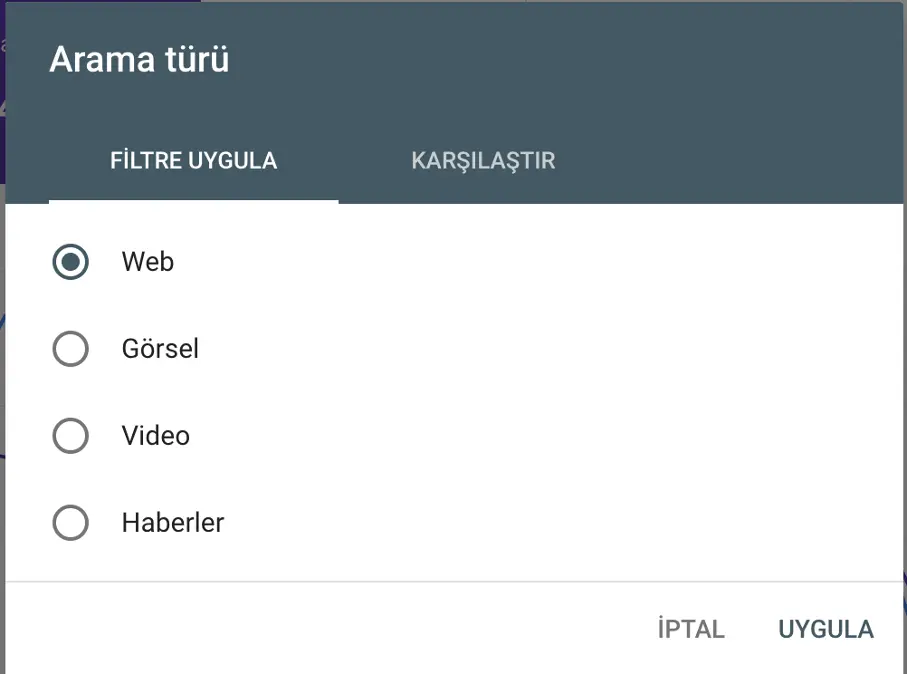
Search Type
Filter performance by search type: Web, Image, Video, or News. You can also compare two search types side by side.
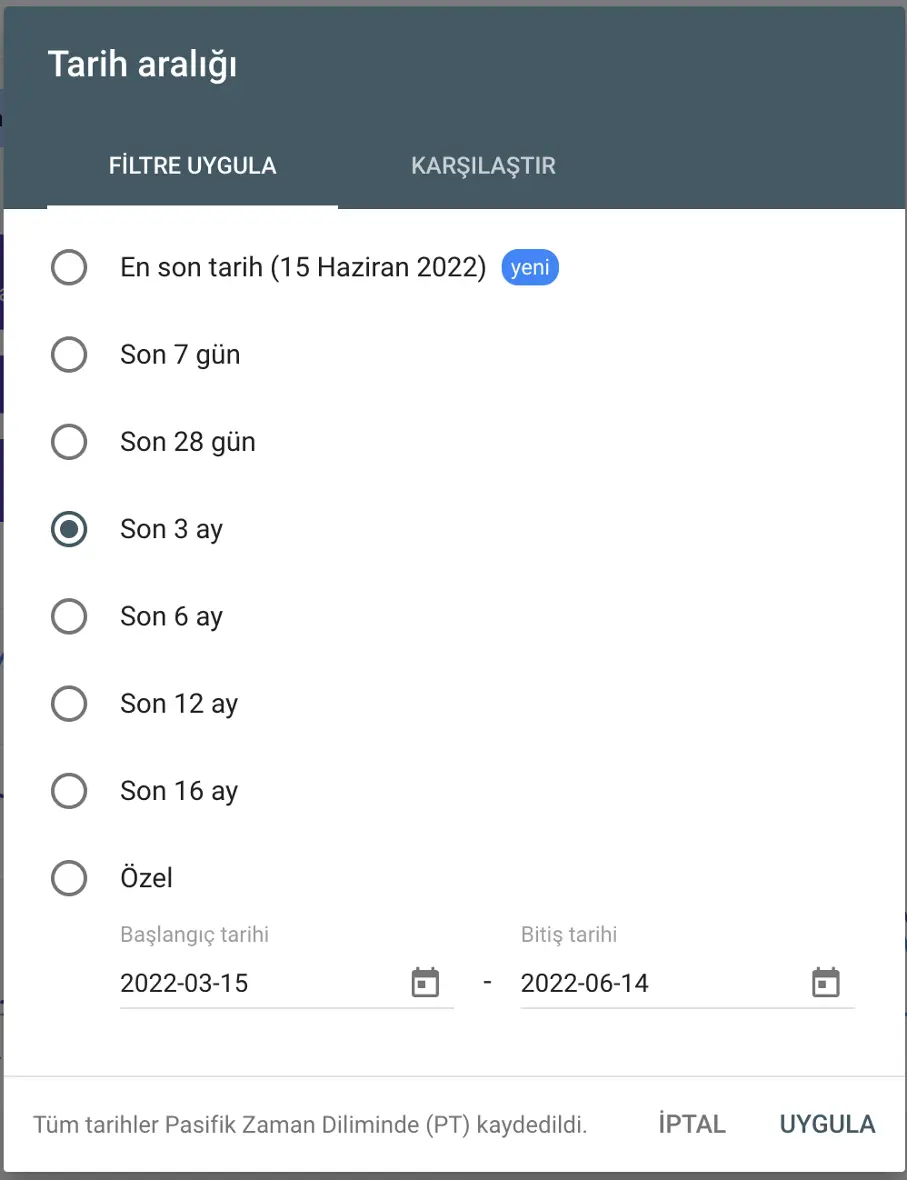
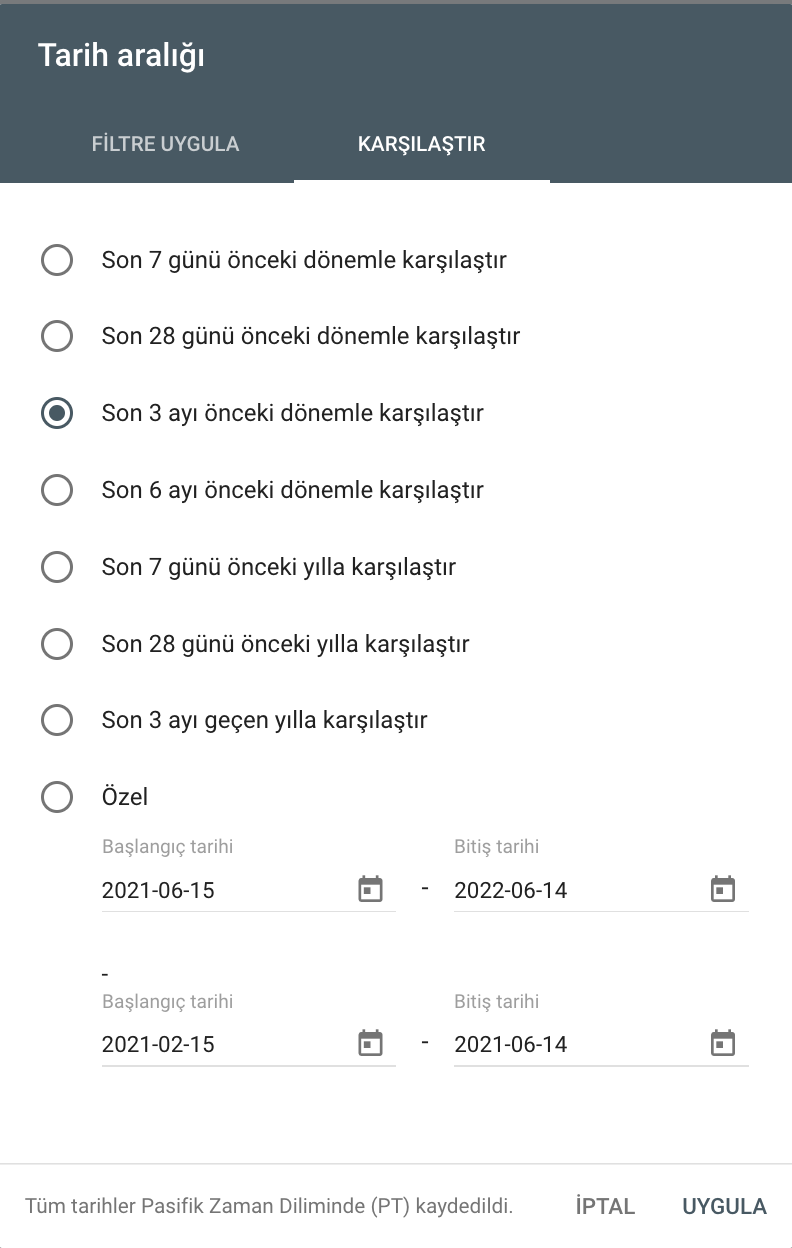
Date Range
Filter data by date range—last 7 days, last 28 days, last 3 months, etc.—or compare two ranges for trend analysis.
Query, Page, Country, Device
Under “New” you can filter by specific queries, pages, countries, or devices (desktop, mobile, tablet).
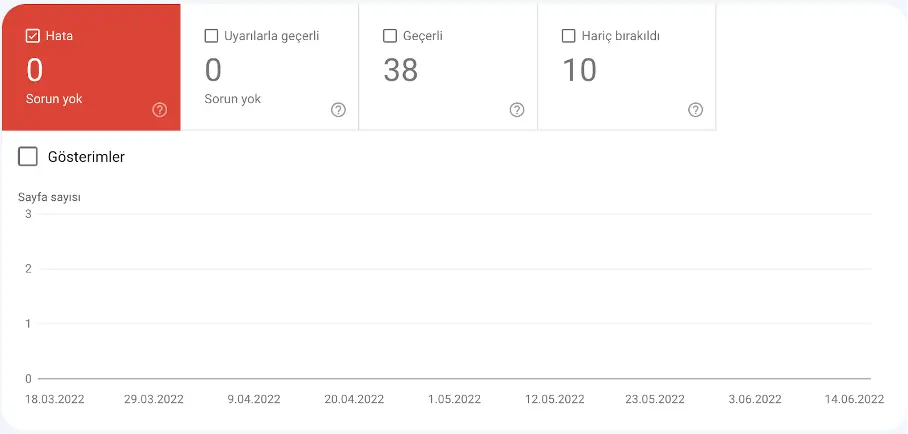
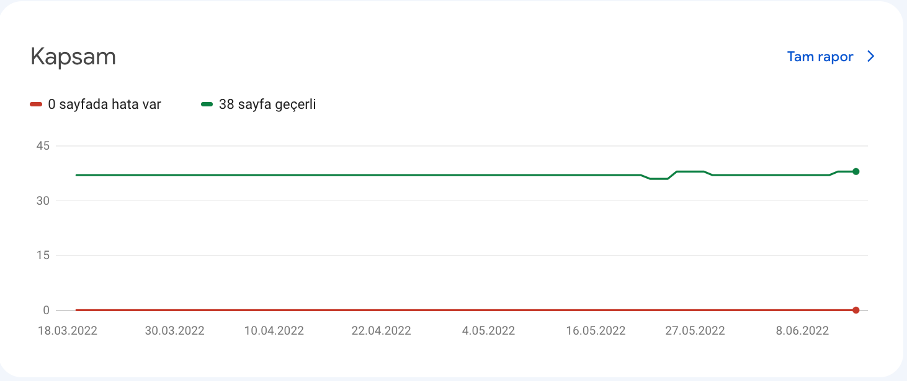
Index Coverage Report
This report shows which pages Google successfully indexed, which have errors, and which were excluded (e.g., due to canonical tags).
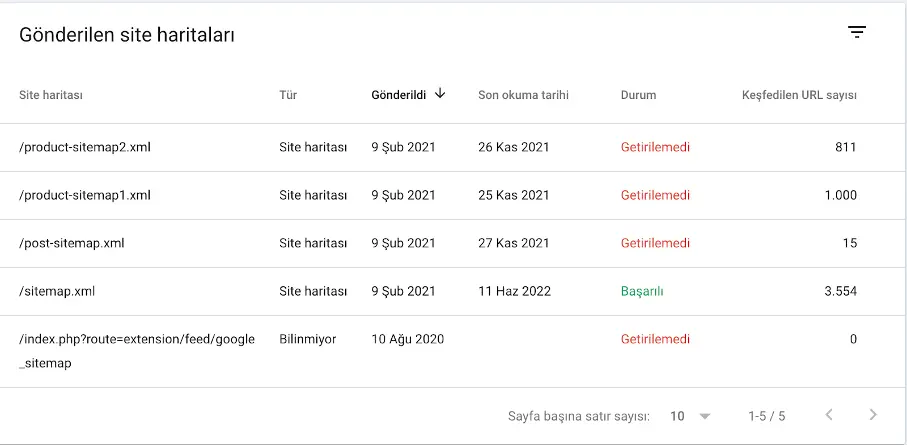
Submitted Sitemaps
See which sitemaps you submitted and whether Google could read them successfully.
Common Uses of Search Console Data
Here are the most frequent ways to leverage Search Console for SEO:
- Identify pages with the most organic clicks
- Find queries with the highest CTR
- Track CTR trends over time
- Monitor impressions over time
- Discover pages with the highest rankings
- Spot pages with declining rankings
- Detect ranking improvements or drops
- Find queries driving the most traffic
- Compare performance across desktop, mobile, and tablet
- Check how many pages are indexed vs. have indexing issues
- Detect mobile usability issues
- See total backlinks
- Identify which URLs have the most backlinks
- Inspect how Googlebot fetches a specific URL
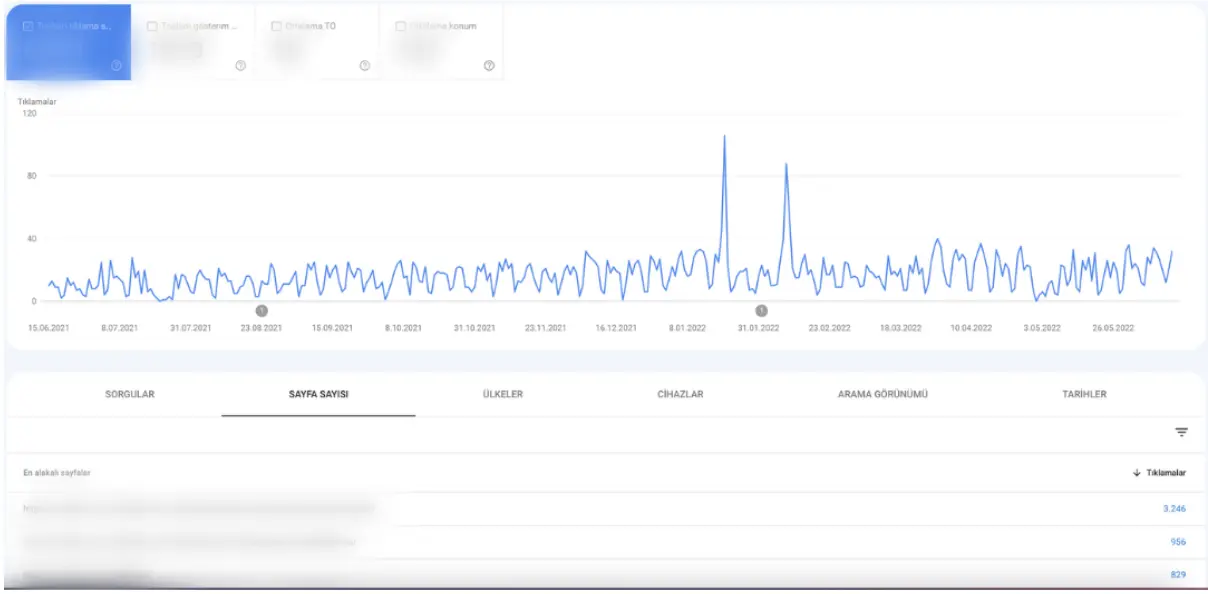
Top Organic Pages by Clicks
Go to Performance → Pages, set your date range (e.g., last 12 months), check only the Clicks metric, and sort descending.
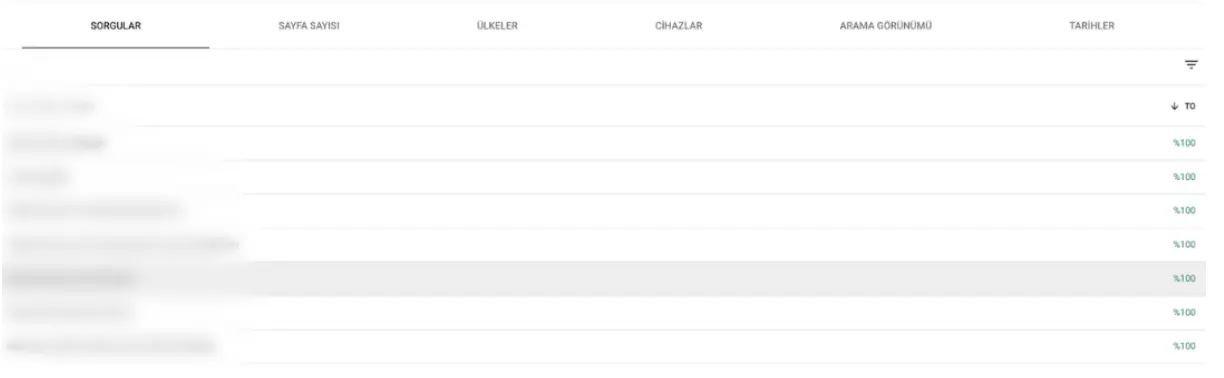
Queries with Highest CTR
In Performance → Queries, set your date range, check only CTR, and sort descending.
Track CTR Over Time
In Performance, view the CTR line chart to catch sudden drops or spikes, which may indicate changes in rankings or impression volume.
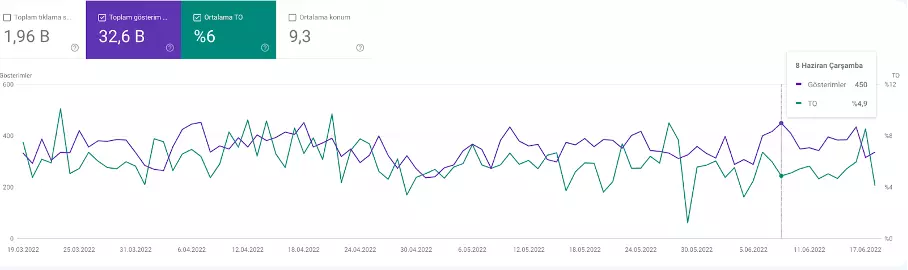
Track Impressions Over Time
Similarly, the Impression chart reveals whether you’re gaining visibility for more keywords or losing ground.
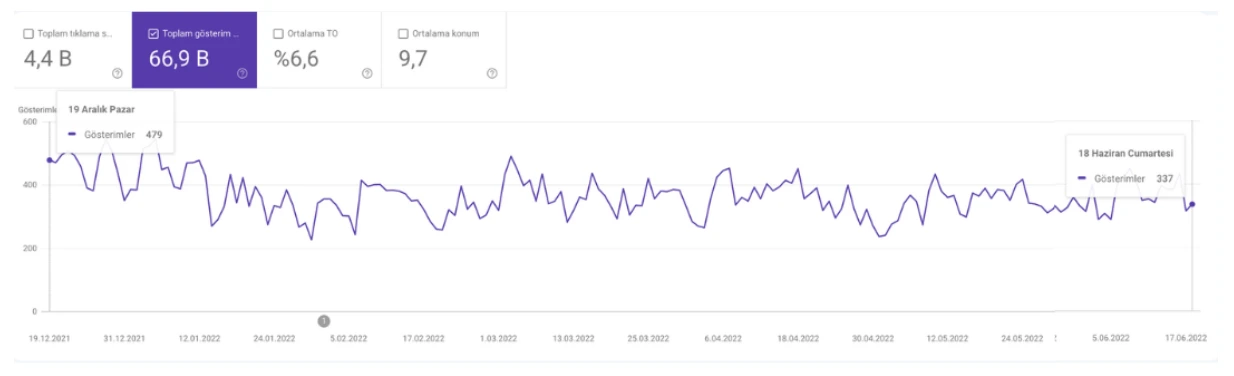
Pages with Highest Average Position
In Performance → Pages, set date range to last 28 days, check only Average Position, and sort ascending.
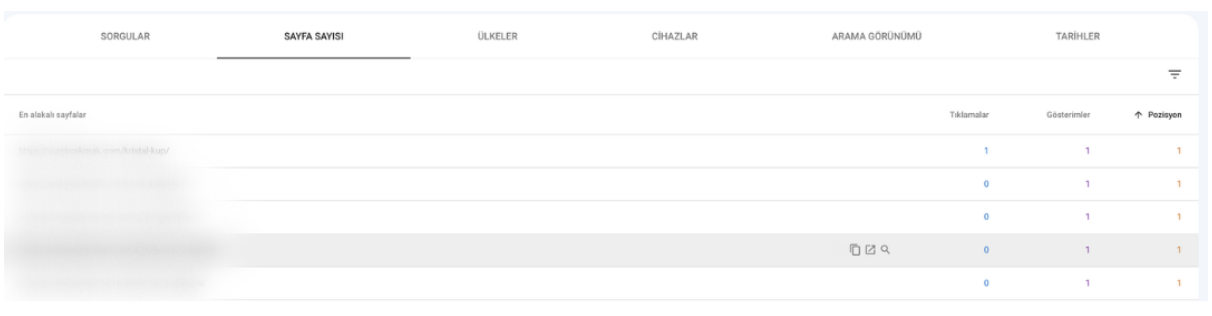
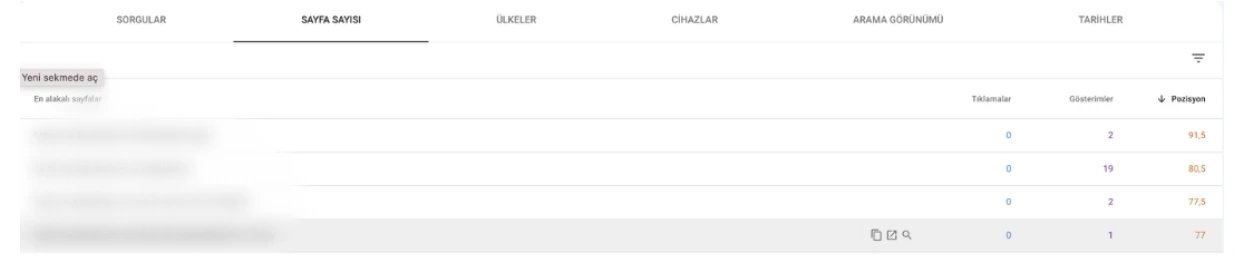
Pages with Lowest Average Position
Same steps as above, but sort Average Position descending to find underperforming pages.
Detect Ranking Changes
Use the date comparison in Performance → Queries to spot keywords that rose or fell between two periods.
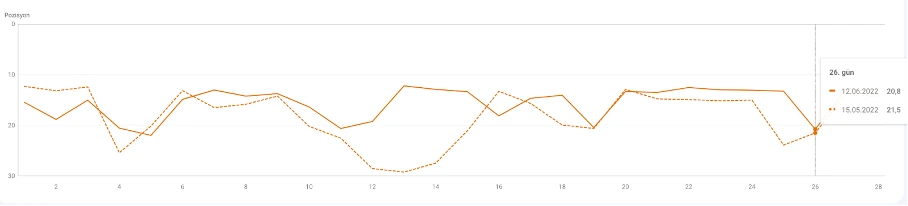
Top Traffic-Driving Queries
In Performance → Queries, set date range, check Clicks, and sort descending.
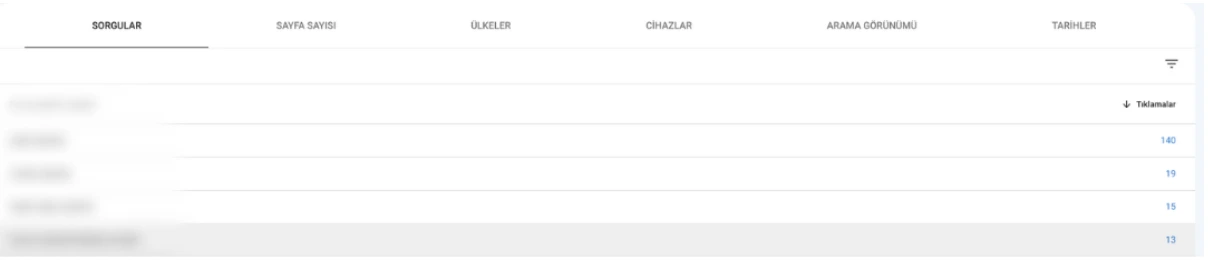
Device Comparison
In Performance → Devices, check all metrics to compare desktop, mobile, and tablet performance side by side.

Indexed vs. Errors
In Coverage, see how many pages are valid (indexed) versus errors (not indexed).
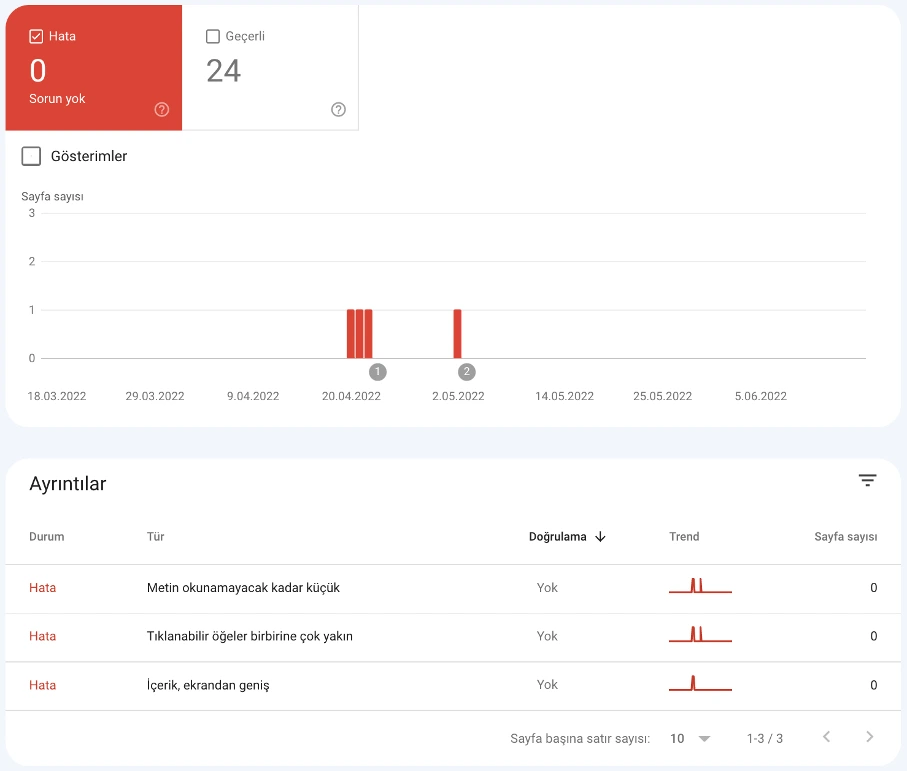
Mobile Usability Issues
In Mobile Usability, view any pages with mobile errors.
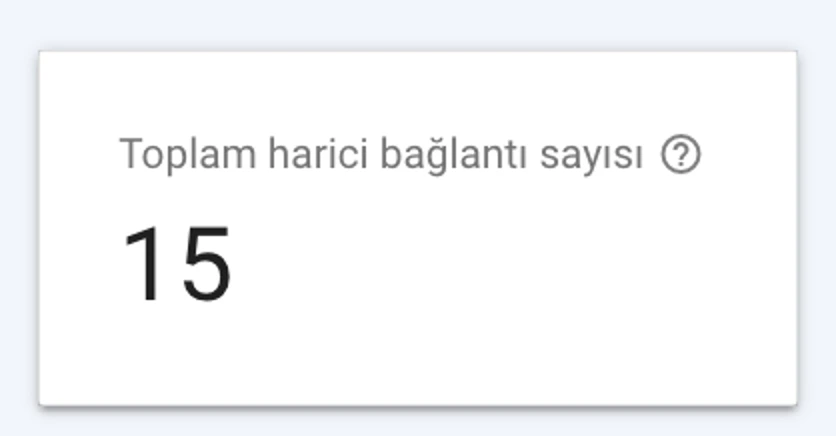
Total Backlinks
Under Links → External, click “More” and view the total number of backlinks.
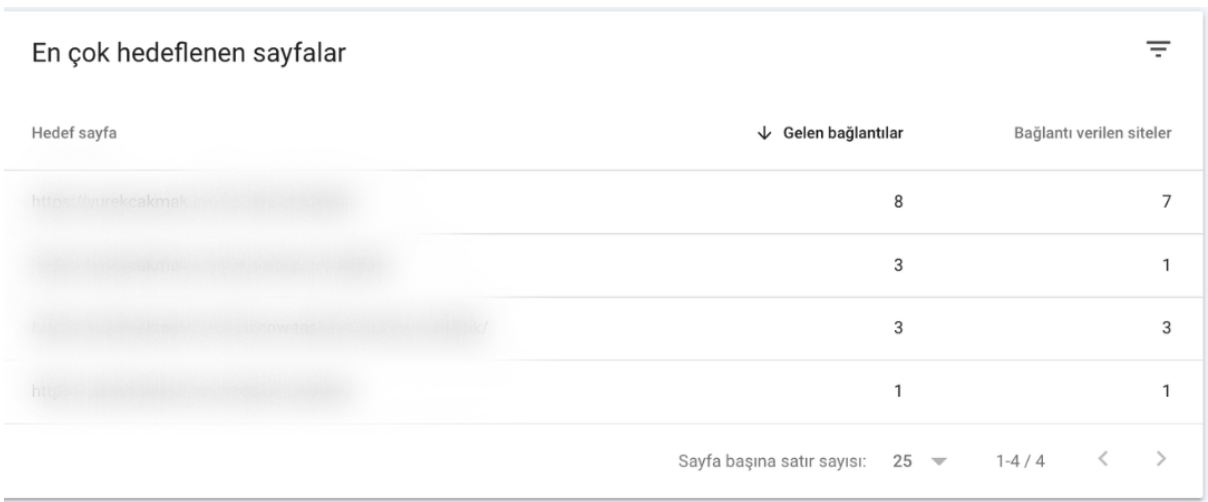
Top Linked Pages
In the same report, sort “Top linked pages” by descending links.
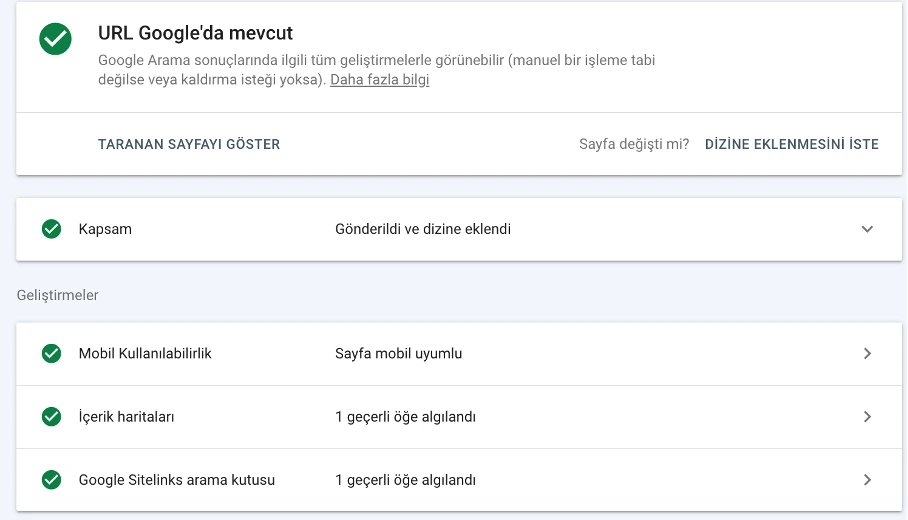
URL Inspection
Use the URL inspection box at the top to see how Googlebot fetches a specific URL and whether it’s indexed.
Conclusion
Google Search Console is an essential SEO tool, playing an active role in diagnosing and improving a site’s interaction with Google search. We’ve covered its most common uses, but Search Console offers much more. As Google continues to enhance this tool, familiarity with Search Console is becoming mandatory for anyone working in digital marketing or web development.
More resources

Generative Engine Optimization (GEO) in the Financial Sector: YMYL Risks and Trust Signals
With the integration of artificial intelligence technologies into the search engine ecosystem, the t...

B2B SaaS Generative Engine Optimization (GEO): A Content and Measurement Model That Increases Demo Requests
The digital marketing world is undergoing a major evolution from traditional search engine optimizat...

What Is a Source Term Vector?
A Source Term Vector is a conceptual expertise profile that shows which topics a website is associat...

