Marketing tips, news and more
Explore expert-backed articles on SEO, data, AI, and performance marketing. From strategic trends to hands-on tips, our blog delivers everything you need to grow smarter.
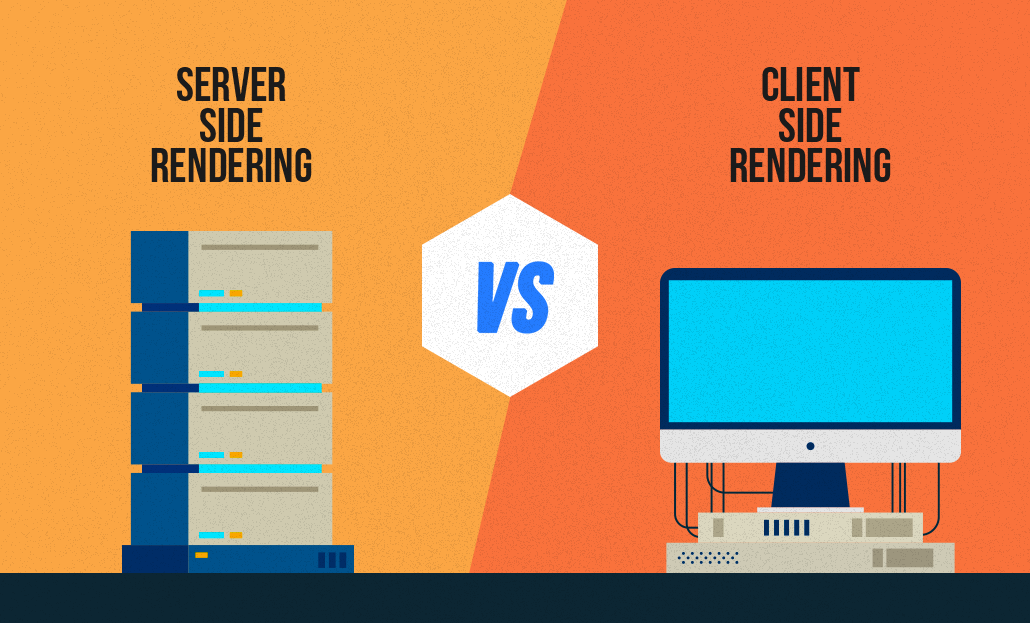
What is Client-Side Rendering (CSR) and Server-Side Rendering (SSR)?
All of the work done for search engine bots to better understand, crawl, and index sites written in Javascript is called Javascript SEO. Analyzing the complete crawlability of text, image, and video content is a top priority for SEO professionals. With the increase of websites written with Javascript, Javascript SEO studies have also started. Modern front-end libraries (React JS, Vue JS, Angular JS, etc.) have paved the way for a new study here. If we go much more fundamentally, as we know, web pages consist of 3 main parts. 1. HTML – We can think of it as the skeleton and content area of your website. A page consisting entirely of Html can give you information but does not offer an attractive design.2. CSS – CSS files that add visuality and design to HTML. Thanks to CSS, we can access the web page design we are familiar with.3. Javascript – It is the programming language that enables movable or changeable areas on a website. When you hover over an area, its color changes, or when you scroll the page, new content is loaded at the bottom thanks to javascript. According to the user's movement, Javascript files are run in the background and the final structure to be shown to the user is presented. With the developments on the software side, websites have recently started to be coded only with JS. Code lines are not presented individually in HTML, but are given directly over JS files. So, how well could Google adapt to these developments?Google & Javascript Relationship Google Javascript sites have started to understand and make sense of it much better in recent years. However, crawling sites written directly in JS is very costly for Google. Compared to a normal site, it both spends more time browsing and exhausts its servers. So what is Google doing to optimize this expense? Google uses a method called 2-stage crawling to crawl pages written in Javascript. In the first stage, Googlebot enters your site, scans the HTML and CSS, and adds it to its index. It also sees the Javascript files here but leaves it to the 2nd time to scan and understand them. In the meantime, it starts to show the results as far as the user sees in the first stage. It puts your site in a row within itself for 2nd wave scanning. This can take hours or days. It evaluates your site in order of its own priority based on its value and authority. When it comes to the 2nd wave, it also scans the Javascript files and adds them to the index. Thus, it starts to show the user the final version that you actually planned. How Is Javascript Different From Other Languages For Google? The browsers we use parse HTML, CSS, and JS through render engines. Therefore, it must be rendered first. Languages such as PHP and Python stand out as languages rendered on the server side. Alternatives such as Angular and React from languages coded with JS can be rendered with both Server Side Rendering (SSR) and Client Side Rendering (CSR) methods. How Does GoogleBot Crawl Javascript Sites There are 2 different methods for the correct crawling and indexing of sites written in Javascript by search engine bots. Client Side Rendering (CSR) (Including Dynamic Rendering) Server Side Rendering (SSR) Client-Side Rendering (CSR) The user or the browser of the search engine makes a request to your address. The server accepts the request and returns the response. The browser downloads the content and accompanying JS files. The browser executes JS files to view the content. The content becomes interactable by users and bots. Pros and Cons of CSR (+) Faster processing after first-page load (+) Puts less load on the server (+) Provides rich site interaction (+) Provides fast website navigation (fewer HTTP requests to the server as it doesn't have to be re-downloaded for every page load) (-) Slower loading of the first page (due to loading of assets required for multiple pages) (-) Delayed loading on devices with low processors. (-) Late loading when the internet connection is weak. (-) It negatively affects SEO if not implemented properly. (The page will appear blank until the Javascript codes are run and the content is created at the opening of the page) (-) External libraries are needed very often. Risks of CSR SEO Your page, which you have prepared using the most modern technologies, may appear as a blank page for Google. If you have a site written with modern Javascript libraries, frequently check how Google understands your site via the "Show Crawled Page" button in the URL Checking tool via Google Search Console. If your page is still not in the Google index, you can also test it on the live URL. Dynamic Rendering Dynamic Rendering is a method used for websites created in CSR to be SEO compatible. The main difference lies in offering different rendering formats to GoogleBot and users. When the server request is made, it is understood whether the request is made via GoogleBot or by the user on the server side. If rendered by GoogleBot, it returns an HTML response that will be rendered on the server. Users continue to view your site as CSR. Server-Side Rendering (SSR) The user or the browser of the search engine makes a request to your address. The server accepts the request, renders the entire HTML and returns the response. The browser downloads the generated HTML and JS files. The content becomes interactable by users and bots. Pros and Cons of SSR (+) Improves user experience by making pages load faster. (+) It is advantageous in terms of SEO. (+) It is a much more ideal structure for sites that offer static content. (+) Fewer JS dependencies are available. (+) Also ideal when the user's internet connection is slow. (-) When the server has a large number of visitors or the site is large, it can cause significant slowdowns in page rendering. (TTFB time may be affected) (-) It has to reload the whole page on each navigation. (-) Server costs will be high to provide higher performance.
How to Check Google Index in 10 Steps?
Updates in search engine algorithms have made many metrics and technical infrastructure important for providing a more successful user experience. In the period from 2015 to 2022, users' mobile and tablet usage increased significantly, while desktop and laptop usage decreased. This situation has caused poor user experiences, especially on sites with large page sources.For example, users visiting a website from mobile devices experience excessive resource consumption and wasted time while loading websites with high-volume images and unused CSS and JS files. This is because the loading times and site speeds of such websites provide an inadequate experience for users, and since the user accesses the site from a search engine, it also causes search engines to lose image.Aware of this, search engines have started to pay significant attention to website speed and resource consumption with the latest updates in their algorithms. To optimize this situation, website owners have strengthened their optimizations in this regard by analyzing the speed and resource consumption of their websites with measurement tools such as Pagespeed and GTMetrix.Pagespeed Page Speed AnalysisAmong the most important performance tools used when optimizing a website, Pagespeed and GTMetrix tools undoubtedly come first. Pagespeed, in particular, developed by Google, shares with us the speed metrics that prevent a successful user experience on websites.One of the metrics that website owners frequently encounter and often fail to solve in Pagespeed analyses is the removal of unused CSS files.Unfortunately, Pagespeed and GTMetrix tools do not share with us which lines in the unused CSS files are actively used, but only provide us with estimated savings and files. This warning alone is not enough to solve this problem.What Are Unused CSS Files?In today's modern web programming technologies, many developers prefer ready-made libraries instead of coding HTML & CSS from scratch. Libraries like Boostrap and Tailwind are examples of these structures. The difference of ready-made CSS libraries is that they collect many button, navbar, grid structure, visual and design commands under certain classes in a single library. In this way, web site developers can easily use all style and CSS arrangements by giving a class to the relevant HTML element, instead of writing separate CSS commands for each structure and module. For example, while many lines of CSS code need to be written to give a button various color and radius styles and hover effects, the desired style arrangements can be obtained by giving a single class since the relevant commands and lines are included in the ready-made library.Although ready-made CSS libraries are very practical for developers, they can cause some problems in SEO-related arrangements as they increase the query and resource consumption on the website. For example, when you include the bootstrap library on your website, you can actively use only 1 or 2 of the 16 different button styles in it. The remaining 14 button styles continue to be included in the CSS file and increase the page's resource consumption even though they are not actively used.In these cases, performance tools that measure speed, such as PageSpeed, inform us that there are actively unused CSS files on the website and ask us to make optimizations related to this.How to Detect Unused CSS Files?There are several ways to detect unused CSS lines on a website. You can use modules like purgeCSS or manually view these lines from the page inspection.To detect unused CSS files, the first thing you need to do is right-click on the page and click on the "Inspect" option.Then click on the three dots on the right side of the window that opens and click on the More Tools > Coverage option.You will see a record button in the section that opens at the bottom. Click this button and refresh the page with CTRL + F5 or Command + F5. After the page is refreshed, you will see that many CSS and JS files have appeared below.The rates on the right side in this section show the unused rate in the relevant CSS file at the moment the page is loaded.When you click on any CSS file, the relevant file opens in the window, and you can again view the unused CSS lines in red and the actively used ones in blue.The important detail here is to determine which code is used on different pages and which lines are active on mobile and tablet devices.How to Remove Unused CSS Files?We learned where to see the unused CSS lines on the website. However, the important part here is to be able to analyze well which CSS line is really used and which is not. Because some CSS lines may be included in a single file for different pages, as well as being included in mobile and tablet devices.For this reason, you should first copy the unused lines from the ready-made library codes in the CSS lines, then navigate to the service, category, product, contact, etc. pages of the site and perform the coverage process we shared above on each page.In addition to this process, you should switch to the mobile and tablet views of your website from the device selection area in the inspect section and, in the same way, visit all pages and copy the unused CSS lines to one side.In the final stage, you can clean the common and actively unused CSS lines among all the CSS lines you have copied.Note: It is recommended that you perform all these operations on the test version of your website and, after performing the cleaning, carry it to the main version if no problems are observed.

What is SEO Title Layout? What Should the Heading Hierarchy Be Like?
One of the metrics frequently encountered in search engine optimization (SEO) work is related to the proper heading structure. One of the questions that people new to or completely unfamiliar with SEO find difficult to understand is what the SEO heading structure should be. When creating an SEO-friendly page, the titles on the page with heading tags are very important. Heading tag types are used to correctly reflect the page content, and to give the user and search engine bots the content parts and focus titles on the page. So why are heading title types so important? In our article, we have included this information for you!What Are Heading Tags?Search engine bots aim to show the most accurate and rich websites with content to users who are searching for a topic. However, since search engine bots are not human, they try to make sense of web sites by scanning them within a certain set of algorithm rules. During this interpretation process, they try to learn what the page content is about and what it explains by taking some metrics as a basis.Heading tags are one of the very important SEO metrics that help search engine bots make sense of the page. Heading tags are usually written in the "" code block and proceed hierarchically from 1 to 6.Why Should We Use Heading Tags?Heading tags are highlight texts that allow the page content to be interpreted by both the user and search engine bots. By default, style structures such as size and thickness are different and more prominent than other text. When interpreting web pages, search engines want the pages to be prepared in accordance with the user's reading and navigation order. This is because providing websites that allow users to access the information they need in the most efficient and practical way increases the reliability and prestige of search engines.For this reason, search engines want page contents to be created in an academic structure and hierarchy. Heading tags play an important role in determining this hierarchy. Because the heading tags added hierarchically on the page interpret the "main topic > sub-topic > sub-heading and description" structure and list the site results in the SERP according to the order of importance within this heading structure for the user performing the search.The use of heading tags not only helps search engines interpret the page, but also allows users visiting the web page to easily access the titles and information texts they need. Therefore, the use of heading tags is one of the most important metrics for creating an SEO-friendly web page.What Are Heading Tags?There are different types and usage examples of heading tags from 1 to 6. These heading types vary from a larger and more prominent style to a more normal and smaller font style according to the number they take. Heading types are as follows: H1: It is the main title of the page. There should be only 1 H1 tag on each page. The H1 tag specifies what topic the relevant page provides information/content about and reflects the main keyword that the page is intended to be visible for in the SERP. H2: These are the topic titles that support the main title of the page (H1). H2 tags refer to the main titles in the page content. H3: These are the subheadings that support the main headings on the page. It is used to specify titles and topics related to that tag under the H2 tag. H4, H5 and H6: They are used to specify subheadings if needed in the page content. For example, if the H3 title and texts used under the H2 main title need to be divided into more subheadings, H4, H5 and H6 headings can be used. How Should the Heading Hierarchy Be?If heading tags are to be used on a web page, these tags must be added hierarchically to the page in a way that ensures topic integrity. For example, if a web page content is created with the title Digital Marketing and this content has subheadings and topics; the heading hierarchy of the relevant content could be as follows:H1: Digital Marketing H2: What is Digital Marketing? H2: Why Digital Marketing? H2: Advantages and Disadvantages of Digital Marketing H3: Advantages of Digital Marketing H3: Disadvantages of Digital Marketing H2: Digital Marketing Courses H3: Which Course Should I Take for Digital Marketing? H4: Udemy Digital Marketing CourseWhat is important when creating the heading hierarchy is that the titles maintain their topic integrity and that the subheadings are always added after the main headings related to that topic. For example, while there is an H2 in the Digital Marketing Courses title, the title Which Course Should I Take for Digital Marketing? should be a subheading of the Digital Marketing Courses title. Therefore, this title is added in the H3 tag and this title should be placed immediately after the Digital Marketing Courses H2 title.Common Mistakes in Using Heading TagsMany websites make mistakes in topic integrity and heading hierarchy when using heading tags in their content. These mistakes make it difficult for search engine bots to interpret and make sense of the page, while also providing the user with an aesthetically inefficient content. Common mistakes when using heading tags are usually as follows:Adding All Content Titles with H2 TagGenerally, due to its style and font size, websites can only use H2 in content titles. However, this is a very wrong method. This is because the style and font sizes of the headings (H2, H3, H4, etc.) can be adjusted with the help of CSS and brought to the desired size and highlighting tones. The main reason for using heading tags in the content is not style and form, but to help search engine bots understand the page hierarchy. Therefore, using all headings within H2 tags is a very wrong method.Using H2 Heading Without Adding Text After H1One of the mistakes many websites make is to add the H1 tag used on the page just for the sake of using it. However, the H1 tag is arguably the most important heading tag that reflects the main keyword of the page content. Therefore, a text content of 100-150 words should be included after the H1 tag. This text content supports the H1 heading tag by providing a summary of the page and the main topic of the page. After that, H2, H3 and other subheadings should be included.Placing All Subheadings at the End of the ContentSome websites misunderstand the heading hierarchy and add all H2 headings first, then all H3 headings on the page. The hierarchy here is related to the topic integrity of the writing and headings. Therefore, using heading types in order on the page is a wrong hierarchy. The correct heading usage structure is as we gave in the example above: Main Heading > Subheading that concerns the Main Heading if any. So, after using H2 and then H3 on the page, if a different main heading that does not concern the used H2 and H3 headings is to be added, it should be added to the page again with the H2 tag.Using Heading Tags in Fixed Areas of the PageHeading tags are often used in many fixed areas on pages due to their form and font size. For example, using heading tags in menu links in the header, in social media links, or in links and category sidebars in the footer is a method that spoils the interpretation of the page content. This is because heading tags are used to ensure the heading hierarchy and topic integrity of the page content. Therefore, for fixed areas and links on pages, instead of headings, span tags can be used and their form and font size can be adjusted with the help of CSS.Hiding H1 Tag with CSSOn many websites, the H1 tag is not wanted to be used because of its font size and form. This is because the H1 tag is the tag with the largest and most prominent font on the page. In this case, websites hide the H1 tag they added just to have used H1 on the page by making it display:none or visibility:hidden with the help of CSS. However, this method is old and provides no benefit. This is because search engine bots can interpret texts and headings that are hidden on the page. Therefore, when the H1 added to the page is hidden with the help of CSS and not shown to the user, it is considered invisible to search engine bots and cannot provide the benefit it should. Instead of hiding the H1 tag added to the page with the help of CSS, the size and form of the H1 tag can be adjusted in the same CSS code line to make it compatible with the page aesthetics.

List of Things to Consider in Blog Posts
You should definitely take a look at this checklist to increase your organic traffic with blog posts tailored to user search intent. With the 13 tips we’ve compiled for you, you’ll ensure search engines understand your content while offering users a great experience.One of the most important channels in content marketing is blog writing.You’re probably familiar with the following advice from SEO experts and content writers: “Create content for users, not search engines.” “Google always rewards high-quality content.” With the 13 recommendations we’ll share, your content can earn respect from both search engines and users.Checklist for Blog WritingYou should carefully review your blog posts. If you want greater visibility and more clicks for a wide range of keywords, certain elements must be considered. Start by checking the fundamentals and then expand your SEO efforts from there. Engaging Content Topics SEO-Friendly URL Structure Create an Author Profile Table of Contents Catchy & Powerful Titles Optimize Your Intro Paragraph Content Headings Ideal Content Length Use of Visuals Summarizing Your Content The Power of Internal Linking Structured Data Markups Display of Related Content 1. Engaging Content TopicsYour blog topics should be engaging for your target audience. When you cover what they’re curious about, they’ll pay more attention to your content and website.Ways to identify engaging topics: Review your site search terms and landing pages via Google Analytics. Ask your sales and marketing teams which questions they frequently receive. Listen to discussions on social media about your industry. You can use these methods or analyze top-performing pages of competitors with tools like Ahrefs to identify the types of content your audience prefers.2. SEO-Friendly URL StructureWe recommend using a simple, short, and memorable SEO-friendly URL for every page on your website.Using dates or long strings in URLs can make them difficult to remember and may negatively affect server response time during crawling.❌ Not Recommended: “https://www.example.com/index.php?id_sezione=360&sid=0108mb202233ah4234”✅ Recommended: “https://www.example.com/seo”An SEO-friendly URL gives both users and search engines a quick clue about the page’s content. Also, remember that uppercase and lowercase letters in URLs are treated as separate pages by Google.3. Create an Author ProfileHaving an author profile for your blog posts is important for E-A-T (Expertise, Authoritativeness, Trustworthiness). Google may use this to evaluate content quality.Listing the author’s name and linking to their profile allows users to easily explore more content by the same writer. For YMYL (Your Money Your Life) topics, author profiles help build credibility.4. Table of ContentsWe recommend adding a table of contents to your blog post, ideally at the top, left, or right of the article.This helps users and search engine bots quickly understand and navigate the content structure.For WordPress sites, you can use plugins like TOC to add a table of contents. Check plugin reviews and download numbers before installation.Tables of contents can also lead to rich results in Google SERPs by showing sitelink text under the main result.5. Catchy & Powerful TitlesYour meta titles (page titles shown in SERPs) significantly influence click-through rates.Titles are important for both SEO and user attention. Relevant and optimized titles improve search performance.Tips for writing page titles: Review Google’s search result pages. Include your brand name. Use numbers where possible. Optimize for search engines, write for users. Revise meta titles for pages with low CTR. Use questions to spark curiosity. 6. Optimize Your Intro ParagraphMeta titles get users to click—but the intro paragraph gets them to stay.Your intro should clearly explain what the content is about and why it’s worth reading. Include stats if possible, and use your target keyword naturally.7. Content HeadingsUse heading tags (H1 to H6) to organize your content. These help search engines and users understand the topic hierarchy.Use keywords naturally in your headings. H1 is the main title, and H6 is the least emphasized.8. Ideal Content LengthContent quality matters more than length. However, the recommended length for blog posts in 2022 is between 1,500 and 3,000 words.Short content is easier to consume, but Google prefers in-depth coverage. Aim for at least 300 words, but consider going longer if your audience prefers detailed insights.Use “read more” accordion menus or A/B testing to gauge reader engagement and refine your strategy accordingly.9. Use of VisualsInclude images and visuals in your blog posts. Sometimes, a graphic or infographic can communicate better than text—especially for complex topics.10. Summarizing Your ContentJust like in school essays, your post should include an introduction, body, and conclusion. A summary at the end helps reinforce your message.Use a call-to-action in your conclusion—like subscribing to a newsletter or browsing a product page—to encourage conversions.11. The Power of Internal LinkingInternal links are essential across your entire site. They help both users and bots explore your content and boost overall SEO performance.Link high-traffic pages to lower-traffic ones to spread visibility. Think of your site as a web of interconnected content.12. Structured Data MarkupsStructured data gives search engines context about your pages. This can lead to rich results in Google and better visibility.Use schema.org vocabulary—especially for product, category, service, or blog pages. For blogs, use BlogPosting or Article. Add FAQ, HowTo, Breadcrumbs, or Recipe where relevant.13. Display of Related ContentIf a user has finished reading a blog post, don’t let them leave your site—show related posts to keep them engaged.Display up to 3 related posts at the end of your article. This not only reduces bounce rate but strengthens internal linking.ConclusionIn this article, we covered 13 essential tips for writing effective blog content. By implementing these strategies, your content will be better understood by search engines and offer users a more optimized experience.If you'd like us to cover more SEO-related topics like this checklist, let us know. If you found this content helpful, feel free to share it on social media to support us!

Screaming Frog User Guide and Configuration Settings
If you want to learn what you can do before you start using Screaming Frog, one of the most frequently used tools by SEO experts, this content is for you.What Is Screaming Frog?Screaming Frog is a tool that scans your website by imitating search engines and allows you to see your website's shortcomings by listing important metrics for SEO. It was founded in 2010 by Dan Sharp. The most important difference from its competitors is that it is Java-based, not cloud-based, and you can install and use it on your computer.There are free and premium versions of Screaming Frog. While the restriction is 500 URLs in the free version, it allows unlimited browsing in the paid version. You can start using it by downloading it from https://www.screamingfrog.co.uk/seo-spider/#download.Obtaining and Activating a Screaming Frog LicenseIf you want to use the premium version instead of the free version, you must obtain a license from https://www.screamingfrog.co.uk/seo-spider/licence/ and enter this license in the tool you downloaded. After entering the user name and license number, you can start using your Screaming Frog program by closing and reopening it.Settings and Configuration OptionsMemory Allocation: Opens to 1GB for 32-bit and 2GB for 64-bit machines as the boot setting in Screaming Frog. If you customize and increase the amount of RAM here, it will allow you to crawl more URLs while in RAM mode.When browsing websites with many pages, you can manually adjust the setting here and increase it, with computers with high memory, you can finish your browsing faster and in a shorter time.Storage Mode: In this section about where the data you scan will be stored and processed, there are two options: Memory Storage and Database Storage. When the Memory Storage setting is selected, all data is stored in RAM, while when Database Storage is selected, storage is provided on the HDD/SSD.Memory Storage Mode is recommended for websites with fewer URLs and machines with high RAM.Proxy Configuration: If you want to use a proxy, you can make settings from this section.Language Configuration: Here you can set the language you want to use the tool in.Screaming Frog Mode SettingsSpider: In this setting, Screaming Frog bots will continue to crawl until they discover all URLs on the website you started crawling.List: This mode allows you to manually specify the URLs you want to crawl. It only scans the URLs you specify.SERP: It provides a preview of how the meta title and description tags of the pages you scan are reflected in the search results.Compare Mode: This mode creates your new scan by comparing it with the previous scan. In this way, you can more easily see which issues have been resolved.Screaming Frog Configuration SettingsSpider: You can select the areas you want or don't want to include before the crawl from the crawl area. You can specify what to exclude with the extraction field. You can configure the limit or depth of your scan in the limits section. You can change the render option in the rendering section to see the data correctly on your JS rendering site. In the advanced section, you can give directions about whether to consider tags such as noindex, canonical, and next/prev. In the preferences section, you can specify or change the pixel boundaries of your meta tags again.Content Area: In this area, you can check the analysis and grammar compatibility of the content on the site you will browse. Screaming frog considers content in the body of a page. It is recommended that you make customizations so that the tool can make more accurate interpretations on a website that was not created using HTML5 semantic elements.Content Duplicates: You can make your custom settings here to test the originality of the content on your site.Spelling & Grammar: Spelling and grammatical errors and the corresponding “Spelling” and “Grammar” options must be enabled for results to be displayed in the Content tab. In this way, you also provide these controls.Robots.txt: You can make the settings related to the crawling of the site you will scan without considering the commands in the robots.txt file in this crawl. You can also create a robots file yourself and have it scanned accordingly.URL Rewriting: You can specify the URLs that you do not want to see in the search results from this field. You can rewrite URLs in the URL Rewriting field. For example, you can reschedule the URLs with the Regex rules you apply to show the URLs with www as non-www or to see the URLs with the .co.uk domain extension in the .com domain extension and see them in the crawl results accordingly. Or, if you want to print your test site URLs, which are in a separate subdomain, as in your live site, this area will be very useful.CDN: The CDN tab is a feature you can use to make Screaming Frog see the URLs of your CDN service as internal links when browsing. After this adjustment, the links of the CDN address will appear in the "Internal" tab in Screaming Frog, and more details will be previewed.Include: The "Include" feature of Screaming Frog can be used when scanning for URLs that will be preferred on sites with a high number of URLs. For this feature to work, the URL from which you start the crawl must have an internal link that matches the regex, or Screaming Frog will not be able to crawl a second URL after the first URL. In addition, the URL from which you start scanning in Screaming Frog must also comply with your matching rules here.https://www.screamingfrog.co.uk/seo-spider/user-guide/configuration/#includeExclude: You can use this feature to exclude URLs, folders, and parameters that you do not want to be crawled while browsing. To exclude URLs from crawling, you need to use Regex language and write commands like this. The exclusions you apply here do not work on the first URL you start crawling on Screaming Frog. The Exclude setting applies only to other URLs discovered during crawling.https://www.screamingfrog.co.uk/seo-spider/user-guide/configuration/#excludeSpeed: In this field, you can set how many URLs the tool will scan per second. The maximum number of Screaming Frog's default settings is 5, and the number of URLs crawled per second is 2. You may need to reduce the browsing speed according to the server performance of the site you are browsing, otherwise, if the number of requests per second is high, you are likely to encounter 500 errors.User-Agent: Before you start scanning, you can regulate which User-Agent you will use to visit the pages with this setting. It may have blocked the Screaming Frog User-Agent on the server side of a website to be scanned. In this case, if you use the Screaming Frog User-Agent, your scan will not occur. You can use this field to check the crawlability of your website in different user-agent options.HTTP Header: The HTTP Header option allows you to scan by providing custom HTTP Header request during a scan in Screaming Frog.Custom Search: The Custom Search section is a feature that allows you to search for any data you want in the source code of a site, thanks to Screaming Frog. You can search HTML for a value you enter as Text or Regex in the Custom Search section. You can check whether the value you entered is in HTML with the "Contains" or "Does Not Contains" options, and you can get the results.Custom Extraction: The Custom Extraction section allows you to extract data from a site's HTML using CSSPath, XPath or Regex. For example, you can access the product codes on the product pages of an e-commerce site with the CSSPath, XPath or Regex settings you will make through this field. The Custom Extraction tool allows you to extract data from working HTML pages that only have 200 response codes. You can switch to JavaScript rendering mode to pull data from HTML rendered outside of a static HTML page.Custom Link Positions: Screaming Frog scans a web page's content, sidebar or footer areas and categorizes each link it discovers based on its location. With the Custom Link Positions tool, you can ensure that the XPath field, which expresses the link positions in the "Inlinks" and "Outlinks" sections in Screaming Frog, works in accordance with the criteria you specify. Thus, you can check whether there is a link in the field you specified.Google Analytics API: By connecting your Google Analytics account with Screaming Frog, you can perform a more detailed scan with your old URLs. To make this connection, you need to click the Google Analytics tab from the API Access menu and then click the “Connect to New Account” button to connect with your Analytics account.Search Console API: For the Search Console connection, you need to click on Google Search Console from the API Access menu and click the "Connect to New Account" button in the window that opens and select your Google account where your Search Console property is located and give the requested permissions. In this way, you can also perform a check for your URLs that were previously discovered and crawled by Google but are not currently on our website.Page Speed Insight API: If you want to see the speed values of your crawled URLs obtained from PageSpeed Insights together with the Screaming Frog scan, you must click on the PageSpeed Insights section of the API Access menu and enter the desired "Secret Key" information before starting your scan. In this way, you will be able to see the speed performance metrics of your crawled URLs in your crawl results.Ahrefs API Connection: If you want to see data from Ahrefs in your scan results, you can connect your Ahrefs account with Screaming Frog. When you click the Ahrefs section in the API Access menu, you need to enter the "Access Token" information in the window that opens.Authentication: If the website you want to scan works after a user log in, you can save your site's user login URL and username & password information to Screaming Frog from the "Forms Based" section in this area. In this way, while scanning, the Screaming Frog bot will first log into your site as if it is a user and will be able to scan for the pages that come after the login screen.

What is Robots.txt and How to Create and Use It?
When search engine bots visit a website, they use the robots.txt file to control crawling and indexing. Also known as the Robots Exclusion Standard, robots.txt tells crawlers which files, folders, or URLs on your web server they may or may not access.You may have heard many misconceptions about how to use robots.txt. In reality, it simply tells visiting bots which URLs on your site they should crawl. It’s used primarily to reduce request load and optimize crawl budget. It is not a way to prevent pages from appearing in search results—that requires a tag or authentication barrier.What Is Robots.txt?robots.txt is a plain-text file placed in your site’s root directory that gives crawlers directives about which URLs (HTTP 200) they may or may not crawl.Bots generally obey these directives. Pages disallowed in robots.txt won’t be crawled, though if those URLs are linked elsewhere, Google may still crawl them.SEO Tip: If bots encounter a 5xx server error reading your robots.txt, they’ll assume something is wrong and stop crawling. That can make images behind a CDN disappear from Google’s view, for example.Why Is Robots.txt Important for SEO?Before crawling your sitemap URLs, bots first fetch your robots.txt. Any incorrect directive can lead to important pages being skipped. A temporary misconfiguration shouldn’t be irreversible—but fix it quickly to avoid lasting harm.For instance, if you accidentally disallow a key category page, it won’t be crawled until you remove the directive. Bots cache your robots.txt for 24 hours, so changes take up to a day to take effect.Where to Find Robots.txtPlace your robots.txt in your site’s root directory (e.g. example.com/robots.txt). Crawlers universally look for it there—never move it.Creating Robots.txtYou can hand-edit robots.txt with any text editor or generate it via an online tool. Then upload it to your site’s root.Manual CreationOpen a plain‐text editor and enter directives such as:User-agent: * Allow: / Sitemap: https://example.com/sitemap.xml Save as robots.txt and upload to your root directory.Recommended DirectivesKey robots.txt commands: User-agent: Selects which crawler a rule applies to. Allow: Grants crawling permission. Disallow: Blocks crawling of specified paths. Sitemap: Points crawlers to your sitemap URL. User-agentSpecifies which bot follows the following rules. Common bots include: Googlebot Bingbot YandexBot DuckDuckBot Baiduspider …and many more. Example: Block only Googlebot from a thank-you page:User-agent: Googlebot Disallow: /thank-you Allow & DisallowAllow: permits crawling. Without any directives, the default is “allow all.”Disallow: forbids crawling of the specified path.Examples: Allow all: User-agent: *Allow: / Block all: User-agent: *Disallow: / Block a folder but allow one subpage: User-agent: * Disallow: /private/ Allow: /private/public-info Testing with Google’s Robots.txt TesterIn Google Search Console, under Index > Coverage, you’ll see any robots.txt-related errors. You can also use the Robots.txt Tester to simulate how Googlebot handles specific URLs.Common GSC Warnings Blocked by robots.txt: URL is disallowed. Indexed though blocked by robots.txt: Page is in the index despite being disallowed—use noindex or remove links. Best Practices & Reminders Bots fetch robots.txt before crawling any page. Use Disallow: to prevent low-value pages from being crawled and wasting budget. Include your sitemap with Sitemap:. Keep robots.txt under 500 KiB—Google only reads up to that size. Test for server errors—5xx responses cause bots to stop crawling. Respect case sensitivity in URL paths. Conclusionrobots.txt is a simple yet critical file for guiding crawlers and optimizing your crawl budget. Ensure it’s correct, keep it at your root, and test any changes promptly.

