
Analytica House
Sep 3, 2022What is JavaScript SEO and How is it Done?

One of the most common problems faced by people doing SEO work is that JavaScript content is not discovered by search engines. If you are dealing with sites built with JavaScript, the issues you encounter will be quite different from classic content management systems.
If you want to succeed in search engines with a JavaScript-heavy site, you need to carry out JavaScript SEO. You must ensure that your site’s pages are created correctly, indexed, and are search-engine friendly.
What is JavaScript?
JavaScript is highly valuable when it comes to web development solutions. HTML and CSS are the foundation, but many developers prefer to leverage JavaScript. The reason is that JavaScript makes it possible to make sites more interactive.
When JavaScript is used, it becomes easier to update the content on pages dynamically. For example, websites that share constantly streaming data like match scores use JavaScript. This way, data is updated in real time with minimal delay.
Without JavaScript, you would need to refresh the page constantly to follow such data. Therefore, even if you build the foundation of the site using HTML and CSS, you need JavaScript to make the site interactive and perform real-time updates.
What is JavaScript SEO?
JavaScript SEO is part of technical SEO work. It is indispensable for sites built with JavaScript. JavaScript usage is quite popular. It is especially used on e-commerce sites to generate main content or to link to similar products.
Despite its popularity, sites built with JavaScript often perform poorly in search engines. The main reason is that JavaScript SEO efforts have not been carried out correctly.
Google Index and JavaScript
Using JavaScript is great for users. However, the same cannot be easily said for search engines like Google. Getting JavaScript content indexed by Google does not always happen. Google’s approach to this is a bit different.
While Google can easily index some content created with JavaScript, it may not index other content. Here, it’s important that the site using JavaScript content is structured correctly. However, you may encounter a similar situation even if your site is built with HTML.
- JavaScript Crawling Difficulty: On HTML sites, crawling content is quite easy. Search engine crawlers scan everything quickly. On JavaScript sites, the crawler visits the site but cannot find the links. It downloads and renders JS files and then examines them.
- Crawler Limitations: Google’s crawler does not always crawl all content. If the content on your site depends on cookies and other stored data, the crawler may not see them. Therefore, it’s not easy to say Google is excellent at JavaScript rendering.
Despite these challenges and limitations, Google continues to improve its search crawler. As long as content is important to Google, it is considered worth rendering. In addition, when the rendering process takes too long, Google’s crawler is designed to skip it.
Is Using JavaScript Bad for SEO?
JavaScript makes it harder to detect various SEO problems because it’s not guaranteed that Google will execute every JavaScript snippet on a page. While trying to make your site successful, you must put in extra effort—and most importantly—apply JavaScript SEO methods.
JavaScript is not entirely bad for SEO. Many sites that use JavaScript extensively still enjoy strong organic visibility. In modern web development, JavaScript is a necessity—just like HTML and CSS.
Is JavaScript SEO Mandatory?
If you own a JavaScript-heavy site, JavaScript SEO is mandatory. Without this work, you’ll struggle to ensure your content is discovered by Google. If the content located within the JavaScript section isn’t discovered, this may also mean the page itself isn’t discovered.
Even though Google is getting better at reading and interpreting JavaScript content day by day, you still need to take the necessary steps to be discoverable. If your site content is tied to JavaScript, you should use JavaScript SEO methods to ensure it gets indexed.
JavaScript SEO: Core Requirements
Once you clearly understand the relationship between JavaScript and SEO, you can take the first step toward JavaScript SEO. If you want your JavaScript-built site to perform well on Google, you should know you must dedicate time to JavaScript SEO.
- Google should be able to crawl your site, understand its structure, and discover its valuable assets.
- Google should be able to render your site without difficulty.
- Google should not consume excessive crawl budget while crawling and rendering your site.
If you want to succeed in JavaScript SEO, you must meet these three requirements. JavaScript rendering is a serious burden in terms of crawl budget. Once you exhaust the crawl budget Google allocates to you, some of your pages will be ignored by Google.
Search-Engine-Friendly JavaScript Content
There are two important ways to check whether JavaScript content is detected and indexed by Google. The quickest method is to use the “site:” search operator. The other method is to check your Google Search Console property. But first, you should perform the following checks:
- Make sure Google can technically render JavaScript content easily.
- It’s not enough to open Google Chrome and check the site. Instead, go to your Google Search Console property and inspect your site with the URL Inspection Tool.
- During checks, verify whether the main content appears. See whether Google can access the related posts or similar products section.
If you notice issues during these checks, you should make the necessary adjustments as part of JavaScript SEO. If Google is having trouble rendering your site, the reasons may include timeouts, various errors, or blocked JavaScript files.
After the basic checks, you should verify whether your site is on Google. To do this, search for “site:https://www.analyticahouse.com/tr/blog/seo-terimler-sozlugu” and check whether the content is on Google.
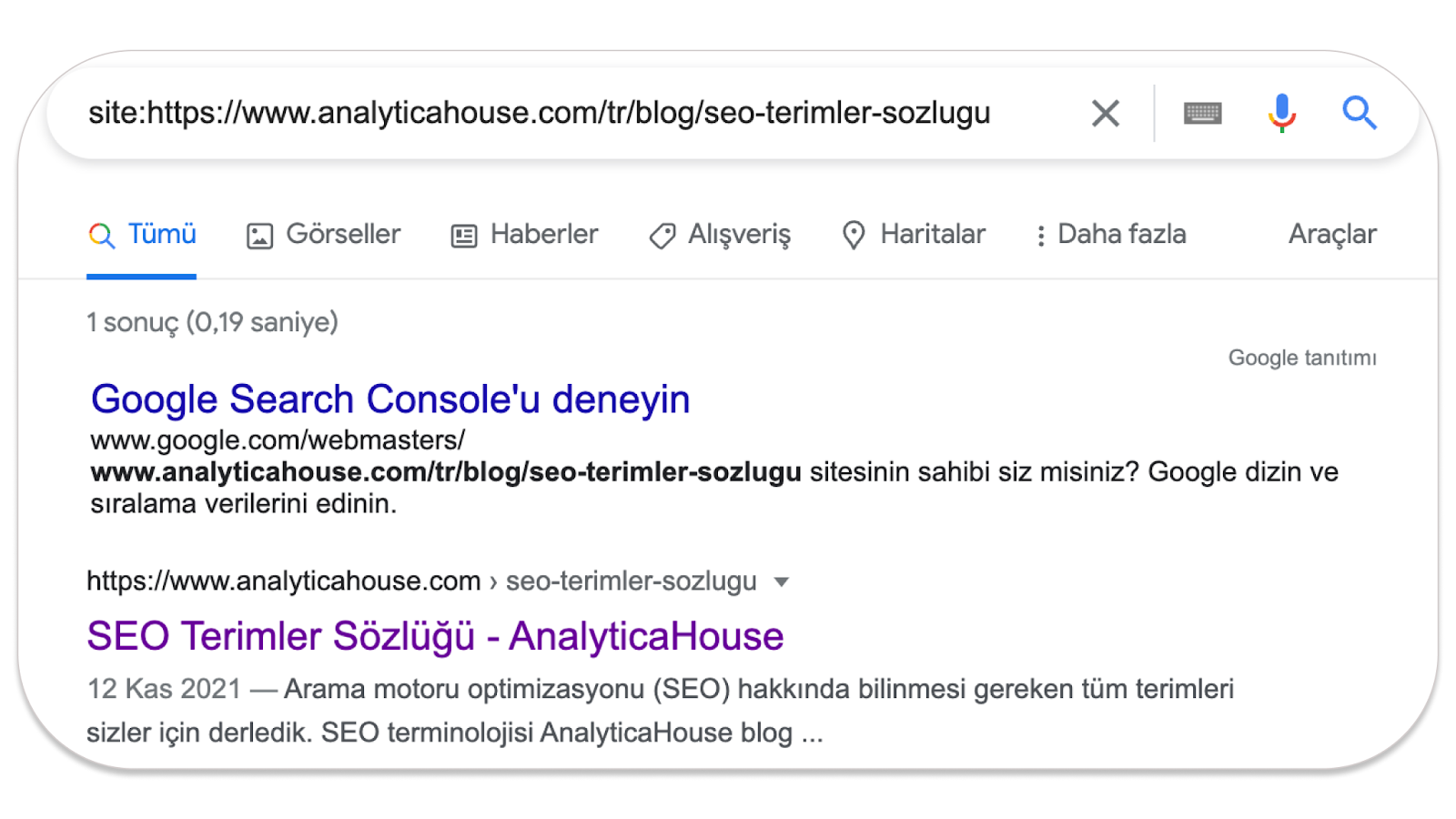
If the URL you checked appears on Google, you can move on to a detailed review. Take the content located in the JavaScript-rendered section on your site and search for it on Google. From this, you can learn whether the JavaScript content has been crawled.
So far, the method we tried was the simplest. However, if you want to perform a much more advanced examination, you should turn to Google Search Console. To perform the necessary checks in your GSC property, follow these steps:
- Log in to Google Search Console and paste the relevant URL into the URL Inspection tool.
- Review the inspected URL and check the content rendered with JavaScript to perform the necessary checks.
- Repeat similar steps for different URLs on your site. Remember that a single URL is not sufficient for verification.
During checks, you may find that JavaScript content is not being crawled. The reasons can include the Googlebot timing out, rendering issues in the content, some resources being skipped, low-quality content, and the page not being discovered.
Delivering JavaScript Content to Google
After making your JavaScript content search-engine friendly, you need to ensure it is delivered to Google correctly. At this point, two different methods are used: server-side rendering and client-side rendering.
- Rendering: Rendering is the process of presenting site content, templates, and other features to the user. Rendering has two types: server-side rendering (SSR) and client-side rendering (CSR).
- Server-Side Rendering: With SSR, when a user visits the site, the page is rendered on the server and sent to the browser. Since JavaScript doesn’t need to be rendered separately, this is generally the most suitable method for SEO.
- Client-Side Rendering: CSR can be problematic in terms of performance. Slow-loading pages negatively affect overall page rankings. To avoid problems, JavaScript SEO methods and CSS should be used effectively.
Some sites use both main rendering methods together. This approach is called dynamic rendering. In dynamic rendering, the site switches between the two rendering techniques depending on who is accessing the site. Thus, pre-rendered pages are served to users.
When JavaScript content is delivered correctly, Google notices JavaScript code immediately and processes it properly. Google’s crawler attempts to crawl millions of sites, so there is a crawl budget allocated to each site.
Google’s crawler handles JavaScript sites in two stages. In the first stage, the crawler looks at the HTML content and evaluates the site using it. Then, the JavaScript that needs to be rendered is processed. When SSR is used, indexing the site is easier.
Anyone who wants to benefit from JavaScript SEO should use as much HTML content as possible. This way, critical information will be sent to the crawler in the first stage, making it possible for the site to be ranked based on that information.
Common Mistakes in JavaScript SEO Work
Although JavaScript is uniquely important in site development, it can be a headache when not used correctly. No matter how good the site is, there will be technical shortcomings if JavaScript is misused. Therefore, you should pay attention to common mistakes when using JavaScript:
Ignoring HTML: The most important information on the site should be delivered with HTML, not JavaScript. Search engine crawlers process the initial HTML. If you want your site to be indexed quickly, create critical information with HTML.
Incorrect Use of Links: Links help people interact better with your site. When using JavaScript, you need to structure links correctly. If the site is structured with JavaScript, Google recommends not using HTML elements for links.
Blocking Google Bots: Unless Google’s crawlers revisit your site, they cannot detect JavaScript code. Some developers use the “noindex” tag, making this revisit impossible. Make sure you don’t have this kind of issue on your site.
JavaScript and Pagination
Many sites use pagination to spread long content across multiple pages. However, most of these sites only allow Google to visit the first page. Therefore, when Google crawls, it cannot notice the other valuable content.
The reason for this error is the link structure. Sites do not use to implement pagination. Instead, they perform pagination based on a user’s click action. As a result, Google’s crawler must “click” to view other pages.
When Google’s crawler visits a site, it does not click or scroll. For Google to notice the next page, links must be used. When links are not used in this way, they are not noticed by Google and your content cannot be discovered.
Use of Hashes and Redirects
One of the most common situations in JavaScript sites is creating URLs using a hash (#). Google may have trouble crawling a page where a hash is used. You should use the correct URL structure to make Google’s job easier.
Incorrect URL: https://www.analyticahouse.com/tr/#/seo-glossary Incorrect URL: https://www.analyticahouse.com/#seo-glossary Correct URL: site:https://www.analyticahouse.com/tr/blog/seo-terimler-sozlugu
If you use incorrect URLs of the types mentioned, you are quite likely to face various crawling problems. Even overlooking a tiny detail means taking a problematic step in terms of JavaScript SEO. You should perform the necessary checks to avoid such situations.
In addition to the use of hashes, you should pay attention to various redirects. If you are implementing redirects via JavaScript on your site, you may run into issues. Therefore, it is much better to perform redirects with server-side 301s.
JavaScript SEO work is part of technical SEO. While trying to improve your site in terms of technical SEO, you should not forget the JavaScript side of things. Not every error is caused by JavaScript. Therefore, performing the correct SEO audits is very important.
More resources

Generative Engine Optimization (GEO) in the Financial Sector: YMYL Risks and Trust Signals
With the integration of artificial intelligence technologies into the search engine ecosystem, the t...

B2B SaaS Generative Engine Optimization (GEO): A Content and Measurement Model That Increases Demo Requests
The digital marketing world is undergoing a major evolution from traditional search engine optimizat...

What Is a Source Term Vector?
A Source Term Vector is a conceptual expertise profile that shows which topics a website is associat...

