
Analytica House
Sep 4, 2022What is Keyword Cannibalization and How to Solve It?
Keyword cannibalization on a website occurs when two or more pages compete with each other for the same keyword or keyword groups, undermining each other’s rankings. Depending on how these pages were created, the solutions will vary.
With the Diversity update, Google aimed to prevent multiple pages from the same domain from filling the top search results for the same query.
What Is the Diversity Update?
Introduced in June 2019, this update took a significant step to curb powerful domains dominating search results. The Diversity update ensures that only one page from a given domain appears in the search results for a specific query, allowing smaller domains to earn organic traffic and offering users more choices. Rather than targeting each keyword with multiple pages as before, the focus shifted to consolidating content into a single strong page that covers the topic comprehensively, which then ranks higher.
https://twitter.com/searchliaison/status/1136739062843432960
Negative Effects of Keyword Cannibalization
- Organic traffic is split between similar pages
- Conversion rates drop and user experience suffers
- Backlink equity is divided among competing pages
- Crawl budget is wasted on redundant pages
What Keyword Cannibalization Is Not
For two pages ranking for the same keyword to truly cannibalize each other, they must both appear in similar ranking positions. If one page ranks well while the other sits far down the results, that is not cannibalization. Addressing a single keyword by consolidating pages can inadvertently remove traffic from other keywords, causing an overall drop. Be sure true cannibalization exists before you act.
How to Detect Keyword Cannibalization
If a page’s traffic suddenly drops or fluctuates, there could be many causes. However, if search volume and average ranking remain stable while impressions and clicks fall, cannibalization may be at work.
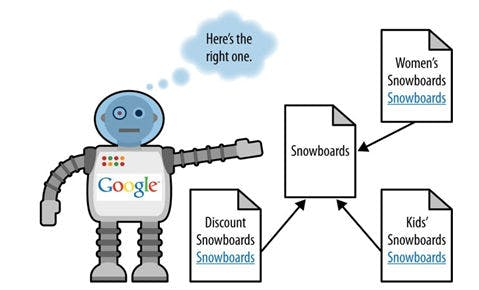
Your goal is to find pages targeting the same queries or serving the same intent. By merging such pages, you can combine their traffic and help the consolidated page climb in the SERPs.
If two pages target similar intent but different queries, differentiate them so each page serves a distinct purpose—for example, user-intent pages for “buy running shoes” versus “running shoe reviews.”
1. Google Search Console
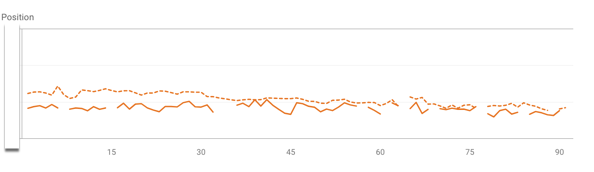
In Search Console’s Performance report, filter by your keyword (Exact Query) and date range. Compare the two URLs in the Queries tab. If you see alternating ranking or traffic drops on one page when the other rises, cannibalization is likely:
2. “site:” Search
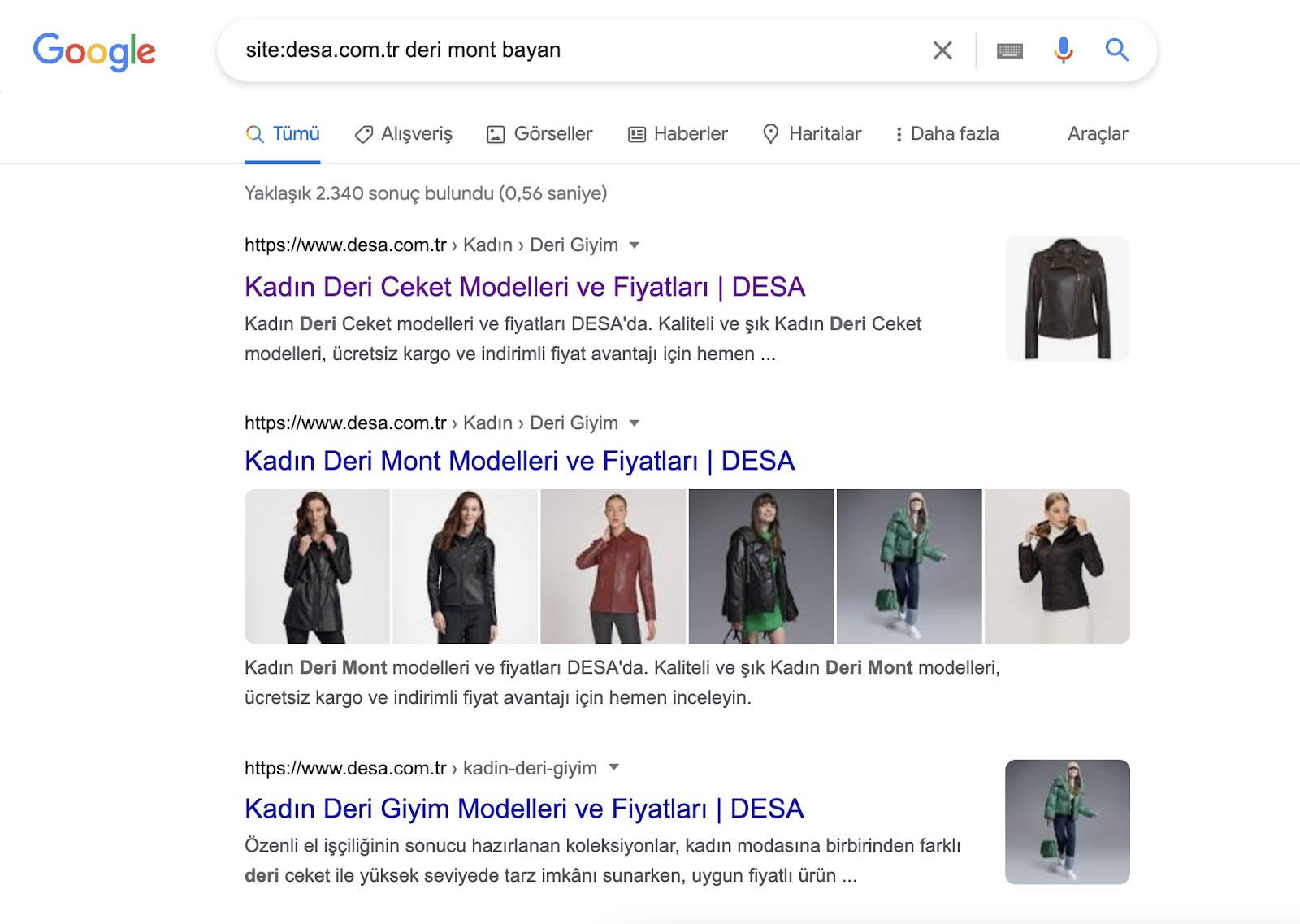
Use a site search (e.g., site:example.com "your keyword") to see which pages are indexed for that term. If multiple pages appear, review them for overlap:
3. Advanced Web Ranking
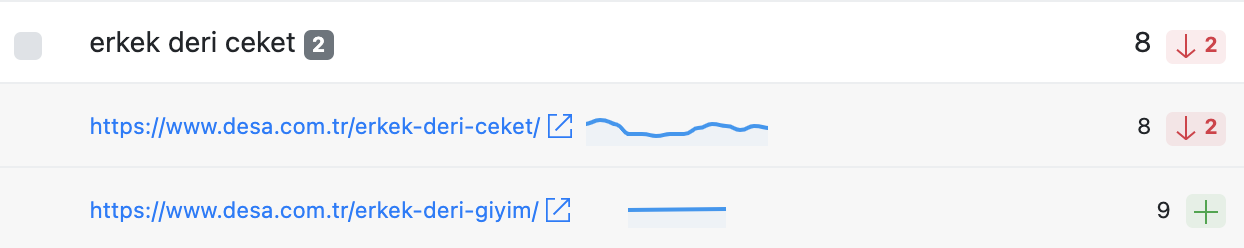
AWR shows how many URLs a domain ranks for a keyword. Multiple URLs indicate potential cannibalization:
4. Ahrefs
In Ahrefs’ Organic Keywords → Movements report, track keyword ranking changes. Sudden swaps between two URLs suggest cannibalization:



Causes & Remedies for Keyword Cannibalization
Cannibalization can stem from various issues; solutions depend on the root cause.
– Duplicate Content
If identical content lives on multiple URLs, consolidate them into one page (301 redirect the rest) so only a single URL ranks.
– Similar Content
Google may treat highly similar pages as duplicates. Differentiate the content, or merge and redirect weaker pages to the strongest version.
– Thin Content
Pages with thin content fail to provide unique value and may be seen as duplicates. Enrich product/category pages with unique details and user intent signals.
– No Dedicated Landing Page
If no page is optimized for a keyword, Google may default to your homepage. Create a dedicated landing page for each target keyword.
– Indexable URL Parameters
Indexable parameters can create multiple URLs for the same content. Use canonical tags, noindex, or Search Console’s parameter handling to address this.
– Internal Linking Structure
Internal links and anchor text guide Google’s understanding. Ensure you link relevant pages consistently to highlight your primary URL for each keyword.
– Backlink Profile
Inbound links and their anchor text also signal relevance. Make sure external links use the correct URL and keyword anchor to avoid splitting link equity.
Conclusion
- Detecting and fixing cannibalization will improve your visibility and rankings.
- Before creating new content, check if you already have pages targeting the same topic. It’s often better to expand and optimize an existing page than to create a new one.
- If no competing page exists, include related keywords and topics to broaden the page’s coverage.
- Optimize internal linking and site hierarchy to focus authority on your primary page for each keyword.
- Offer a single, comprehensive, and well-optimized page for each search intent.
More resources

Generative Engine Optimization (GEO) in the Financial Sector: YMYL Risks and Trust Signals
With the integration of artificial intelligence technologies into the search engine ecosystem, the t...

B2B SaaS Generative Engine Optimization (GEO): A Content and Measurement Model That Increases Demo Requests
The digital marketing world is undergoing a major evolution from traditional search engine optimizat...

What Is a Source Term Vector?
A Source Term Vector is a conceptual expertise profile that shows which topics a website is associat...

