
Adem Mert Kocakaya
Sep 4, 2022What Are HTTP Status Codes? A Comprehensive Guide to HTTP Status Codes

HTTP is a type of communication protocol that enables the distribution and interpretation of a specific resource and data. The fundamental protocol that ensures the data flow of websites is built on HTTP. When we visit a web page, the data included from a different source, the loading of the page, and its interpretation by the browser—in short, all the data delivered to the user—are carried out via the HTTP protocol.
For the HTTP communication protocol to be better interpreted by developers and bots, there are various response codes. These response codes are expressed as numerical values, such as 200, 301, 404, etc.
What is the Difference Between HTTP & HTTPS?
One frequently asked topic is the difference between HTTP and HTTPS. HTTPS here is not a different protocol from HTTP. The "S" at the end indicates that the related HTTP port has an SSL certificate. The SSL certificate ensures that the data transferred via the HTTP protocol is encrypted.
This way, user information, cookies, payment, and personal data are encrypted and stored in the browser’s cache and cookies. If any third party accesses this data, they encounter encrypted text. Thus, user browsing is made secure.
Search engine algorithms require websites to have an SSL certificate on their HTTP protocol. The SSL certificate, which is an important metric for SEO efforts, is also taken into account by browsers. When you visit a website without an SSL certificate, you encounter the label "Not Secure."
What are HTTP Response Codes?
The HTTP communication protocol may encounter issues while loading data in certain situations, or there may be problems or parameter requirements in the URL where a GET/POST request is made. In such cases, the HTTP protocol uses response codes to describe the situation. These codes consist of numerical values.
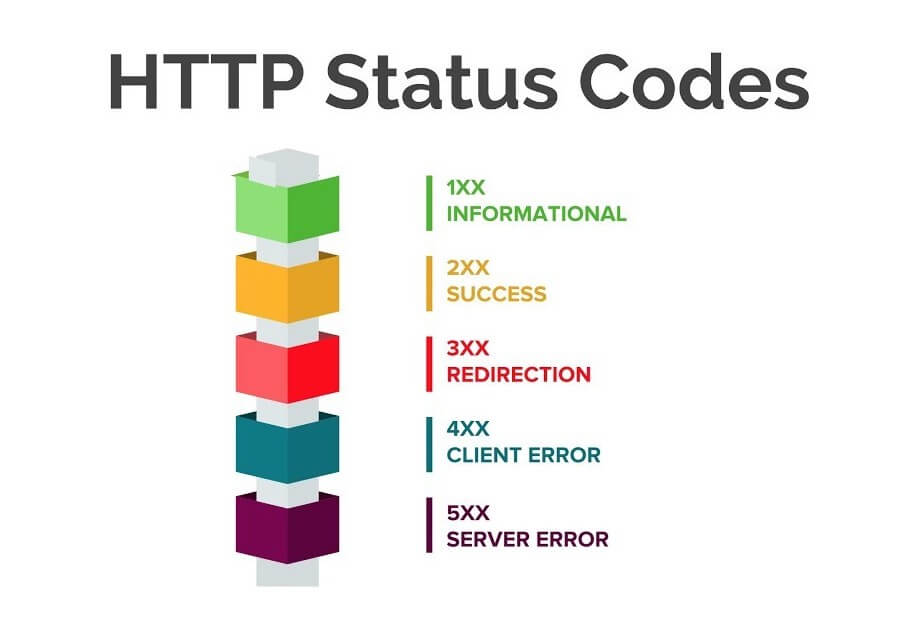
200 Response - OK
A 200 HTTP response indicates that the page has successfully loaded. If there is no issue with data transfer, the 200 status code is usually returned.
204 Response - No Content
Pages that generally have no content return the 204 response code.
301 Response - Moved Permanently
A 301 HTTP response indicates that the related URL has permanently redirected to another URL. Typically, permanent redirects with the 301 response code are applied to prevent closed/errored pages from losing authority in search engines.
302 Response - Moved Temporarily
The 302 response code indicates that the related URL has been temporarily redirected to another URL and will be reactivated after a certain time. This way, search engine bots do not remove the URL from their index and do not strip it of authority.
400 Response - Bad Request
A 400 HTTP response is the status code returned when excessive or malicious requests are made to a page. For example, in spam login attempts, bot CURL, and data extraction processes, some servers return a 400 response code for security purposes.
401 Response - Unauthorized
On websites, if an attempt is made to access a URL that requires user/admin login, session, or token without authorization, the 401 status code is returned. It indicates unauthorized access.
403 Response - Forbidden
The 403 response code indicates that access to the related URL is not permitted. For example, when direct access is attempted to a page that requires login via a token, password, or ID, the 403 response code is generally returned.
404 Response - Not Found
A 404 HTTP response means that the data related to the URL was not properly delivered, and the page could not be loaded. When a URL returns 404, it means that the URL is now a broken link.
405 Response - Method Not Allowed
A 405 HTTP response indicates that the request was made with the wrong method/data to the requested page. For example, when a GET request is made to a page that requires the POST method, the 405 status code is returned.
500 Response - Internal Server Error
The 500 response code indicates a server-side issue on the website that prevents the page from loading.
503 Response - Service Unavailable
A 503 HTTP response is the status code returned when the server is overloaded, bandwidth decreases, etc. It indicates that the server is under heavy strain during the visit.
Other HTTP Response Codes
In addition to the most common ones, the following status codes are also used in HTTP responses.
- 100 - Continue
- 101 - Switching Protocols
- 102 - Processing - webDAV
- 201 - Created
- 202 - Accepted
- 203 - Non-Authoritative Information
- 205 - Reset Content
- 206 - Partial Content
- 207 - Multi-Status - WebDAV
- 210 - Content Different - WebDAV
- 300 - Multiple Choices
- 303 - See Other
- 304 - Not Modified
- 305 - Use Proxy
- 307 - Temporary Redirect
- 402 - Payment Required
- 406 - Not Acceptable
- 407 - Proxy Authentication Required
- 408 - Request Timeout
- 409 - Conflict
- 410 - Gone
- 411 - Length Required
- 412 - Precondition Failed
- 413 - Request Entity Too Large
- 414 - Request-URI Too Long
- 415 - Unsupported Media Type
- 416 - Requested Range Not Satisfiable
- 417 - Expectation Failed
- 422 - Unprocessable Entity
- 423 - Locked
- 424 - Method Failure
- 451 - Unavailable For Legal Reasons
- 501 - Not Implemented
- 502 - Bad Gateway
- 504 - Gateway Timeout
- 505 - HTTP Version Not Supported
- 507 - Insufficient Storage
More resources

Generative Engine Optimization (GEO) in the Financial Sector: YMYL Risks and Trust Signals
With the integration of artificial intelligence technologies into the search engine ecosystem, the t...

B2B SaaS Generative Engine Optimization (GEO): A Content and Measurement Model That Increases Demo Requests
The digital marketing world is undergoing a major evolution from traditional search engine optimizat...

What Is a Source Term Vector?
A Source Term Vector is a conceptual expertise profile that shows which topics a website is associat...

