
Adem Mert Kocakaya
Sep 3, 2022What Should You Pay Attention to in SEO Compatibility When Creating a New Website?

When building a website, it is the best time to make the easiest optimizations and infrastructure setups in terms of search engine compatibility. Many SEO metrics such as speed, visuals, canonical and meta editing can be easily organized during the website construction phase, coded within certain rules, and provide great convenience after the website goes live.
1- Speed Factors
Speed is one of the most important factors for successful search engine optimization and user experience. Among the most obvious factors affecting the speed of websites are:
- Visual & Media Content
- CSS Files
- JS Files
- Server Quality
When preparing a website, first of all, all the images on the site must be optimized and sized in a way that does not compromise efficiency. For this, it is important to use images in WebP, JPEG2000, JPEG, SVG formats. Since the WebP format is not displayed in Safari browsers, the “on-error” function can be used in the HTML part so that the JPEG version of the image is shown in Safari browsers while the WebP format is shown in other browsers (Chrome, Mozilla, Opera, etc.).
It is extremely important that visual and media content is optimized as much as possible. Compressing images under 150 KiB positively affects browser loading speed.
It is also important that visual and media content is not larger than the area in which they are placed. For example, if an image is to be added to an average 400x400 pixel area in a grid module on the homepage, the image should not be larger than 400px. Otherwise, while the image covers an area of 400px in the browser, it will load with higher size and resolution during loading, which will negatively affect the opening speed.
The most obvious mistake made with JS (JavaScript) and CSS files is the use of ready-made JS and CSS libraries without optimization. For example, the jQuery JS library or the Bootstrap CSS library contains many classes and functions. However, we generally use only a few of these classes and functions in our websites. Therefore, before being included on the page, unnecessary classes and functions should definitely be cleaned from these files and compression operations should be performed.
Another factor affecting website speed is server quality. When a user visits a web page, the loading of DOM elements on the page by the server and the late response of request queries by the server negatively affect page performance. Therefore, it is important for the website to be hosted on a quality server in terms of processor, CPU, and RAM, and to have high bandwidth.
2- Meta Edits
A web page has indispensable metas. Meta title, meta description (meta keywords for search engines other than Google) are the main ones. First of all, the meta title and description fields must be editable and customizable on the CMS side. However, since a page's metas must not be empty, and sometimes some pages may be overlooked, if no custom meta description is entered, metas can be generated by defining a rule. For example:
Page H1 + Site Name
In this way, on forgotten/overlooked pages, instead of meta tags appearing empty, they will be generated based on a standard rule. Meta tags must be included among the tags of the page.
3- Canonical Tagging
Canonical tags are one of the most important markers that determine a web page's crawling and indexing criteria. To avoid duplicate page issues on websites and to indicate whether a page is its original version or another version, canonical tagging is used.
Canonical tagging must be editable and customizable on the CMS side. However, since there may be pages that are forgotten or overlooked, just like in meta edits, canonical tagging should be created on all pages by defining a rule. For example:
In this way, canonical tagging that automatically points to itself will be created on all pages that are not optionally edited. Canonical tagging must be included among the tags of the page.
4- H1 Heading Tag
The H1 heading tag is the main title of a web page. It directly carries the targeted keyword of the relevant page and reflects the title of all the content on the page. Each page must have exactly 1 H1 tag. H1 tags must be editable and customizable on the CMS side. However, as in meta and canonical, a rule can be defined so that it does not appear empty on pages where it is forgotten to be edited. For example:
Page Name
There must be a maximum of 1 H1 heading tag per page. Therefore, if there are areas on the page that contain different H1 tags, these areas should be defined with
or
tags instead of H1.
5- Robots.txt File
The Robots.txt file is a kind of entry navigation that search engine bots first visit on a website. The pages/folders that are desired to be crawled or not crawled within the site, and the path of the sitemap, are specified in the robots.txt file. The line starting with the “Allow” command indicates a crawlable web page, while the “Disallow” command indicates pages that are not desired to be crawled. The “User-agent” command specifies which bots the commands will apply to. For example, a website can be open to crawling for Google bots but closed for crawling bots like Screaming Frog. The “*” symbol means that commands apply to all bots. For a web page with an admin panel, a standard robots.txt file can be created as follows:
User-agent: * Allow: / Disallow: /admin Sitemap: https://sitename.com/sitemap.xml
The Effect of Robots.txt on the Site
When a robots.txt file is created, the commands defined here must have a dynamic effect on the pages within the site to help with the crawl budget.
For example, we give disallow to the /myaccount URL in the robots.txt file to block it from crawling. In this case, to help search engine bots, a “nofollow” tag should be dynamically added to all links pointing to the /myaccount address within the site. Otherwise, search engine bots may crawl a page that should not be crawled in robots.txt by following internal links. This negatively affects the crawl budget.
In addition to the nofollow tag, if a page is disallowed in the robots.txt file, a meta robots tag should be added directly into this page. Example:
Pages disallowed in the robots.txt file should also not be included in the sitemap. All of this process should be dynamically created during website construction. If a page disallowed in robots.txt is linked within the site, adding nofollow to all of them and adding a meta robots tag to the page itself should be dynamic.
6- Sitemap – Sitemap.xml
The sitemap is a kind of navigation file that facilitates navigation and crawling for search engine bots visiting the website. Sitemaps should be generated dynamically, not manually. All pages listed for the user, such as service, blog, product pages, should be included in the sitemap.
Of course, while generating the sitemap dynamically, the primary factor must be the robots.txt file. If a page/URL is blocked from crawling by adding disallow in the robots.txt file, this page/URL must not be included in the sitemap.
Sitemaps must be in .xml extension and readable. For an example sitemap model, you can visit Google documentation:
https://developers.google.com/search/docs/advanced/sitemaps/build-sitemap
7- Pagination & Infinite Scroll Usage
Especially in e-commerce sites’ product listing and blog listing pages, pagination must be used. Listing all products/content of a category on the same page when a category page is visited negatively affects browser performance and user experience.
To prevent this and increase page efficiency, a pagination structure should be used on the page. There are several types of pagination. For example:
Pagination done by page numbering:

Or infinite scroll pagination, where content loads as the page is scrolled. Among these types of pagination, the most widely used today are Load More and Infinite Scroll pagination. Because instead of directly switching to different pages, content/products loading as the page is scrolled increases the user experience. Today, Google is also switching to infinite scroll pagination and recommends it. Example Google documentation:
https://developers.google.com/search/blog/2014/02/infinite-scroll-search-friendly
8- Language / Hreflang Tags
If a website uses multiple language options, hreflang tags must be used on the site to avoid duplicate issues and to ensure more relevant results in location-based searches. These tags should mark the alternative language pages on each language page. For example, if a web page that opens in Turkish by default has an English version:
The hreflang to be placed on the Turkish page:
The hreflang to be placed on the English page:
9- Structured Data Markup
Structured Data Markup is a kind of schema markup that allows a web page to be more easily interpreted by search engines.
There are many types of structured data markup for web pages. To give examples of the most commonly used structured data markups:
Organization Markup
Organization markup is a type of markup that should only be placed on the homepage of a website and represents the business card of the website. This markup includes the organization of the website, contact information, etc. Organization markup can be done as follows:
Breadcrumb Markup
Breadcrumb markup is beneficial because it presents the existing breadcrumb structure more neatly to search bots, so we strongly recommend using it on all pages to show hierarchy.
The breadcrumb markup to be placed on all inner pages should mark all categories that precede it hierarchically. Example:
Product Markup (For E-Commerce Sites)
Product markup is used for product pages and directly contains information about the product. Example:
Service Markup (For Service Pages)
For sites that sell services in consulting, education, etc., service markup can be used instead of product. Example usage:
BlogPosting Markup (For Blog Pages)
BlogPosting markup is used for blog pages on the website. Example usage:
FAQ Markup (For FAQ Pages)
FAQ markup is used for frequently asked questions pages on websites. The most important benefit of this markup is that it appears in search results, called Google snippets.
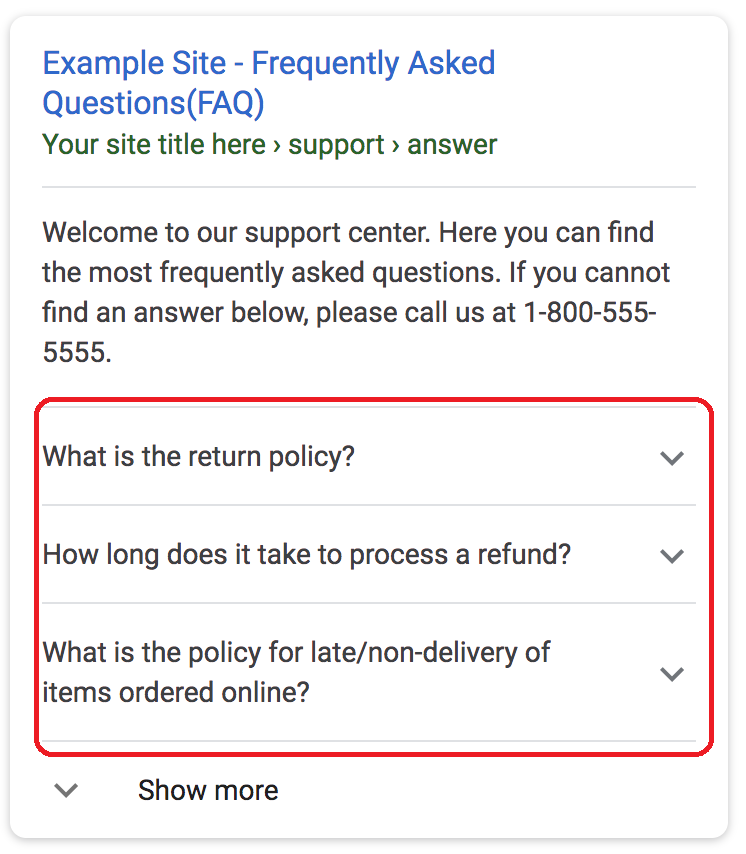
Example FAQ markup usage:
10- Breadcrumb Structure
Breadcrumb is a type of header navigation that makes site navigation easier. It is a structure that allows users to see hierarchically which page they are on, which category the relevant page belongs to, and to easily navigate between categories and pages.
The breadcrumb structure must be created dynamically and placed at the top of the page. An example breadcrumb usage may look like this:

An example for e-commerce sites:
Home > Category > Product Name
For more information, you can visit the W3 documentation:
https://www.w3schools.com/howto/howto_css_breadcrumbs.asp
More resources

Generative Engine Optimization (GEO) in the Financial Sector: YMYL Risks and Trust Signals
With the integration of artificial intelligence technologies into the search engine ecosystem, the t...

B2B SaaS Generative Engine Optimization (GEO): A Content and Measurement Model That Increases Demo Requests
The digital marketing world is undergoing a major evolution from traditional search engine optimizat...

What Is a Source Term Vector?
A Source Term Vector is a conceptual expertise profile that shows which topics a website is associat...

